Embedded finance promises a world where businesses never need to walk into a traditional bank. Through third-party providers, they can manage their banking needs: opening accounts, getting debit cards and securing financing.
These providers aren't run by banks but by tech-savvy embedded finance platforms. They collaborate with banks and tech companies to weave financial products into a unified, user-friendly experience. This is the core of embedded finance, a synergy of banking, commerce, and business services.
We take a look at embedded finance and fintech, the key use cases, and forecasts for future growth.
What is Embedded Finance?
Embedded finance is placing a financial service into a non-financial platform, journey or experience. Think of an e-commerce website providing insurance services or a retailer-branded with a credit card. Embedded finance is becoming more common as it improves customer experience, becoming a natural extension of a non-financial service.
How Embedded Finance Works
Embedded finance is streamlined by third-party firms such as Banking-as-a-Service. They enable non-financial companies to provide financial services without acquiring a license. This is made possible by integrating the services of licensed financial providers into their products and platforms.
The whole ecosystem is built on Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). They act as a software bridge, allowing different entities to communicate with each other and securely transfer data.
Open Banking & Embedded Finance
Embedded finance tools took off amidst the rapid digitisation of financial services. The open banking framework, enforced in Europe by the PSD2 regulation in 2018, mandated traditional banks to share data with licensed fintech companies, provided they have obtained consumer consent.
Embedded Finance Use Cases
As finance covers a wide array of activities, so does the range of embedded financial services.
When implementing embedded finance, businesses should clearly understand what services they want to integrate and why. Generally, embedded finance is divided into six sub-categories.
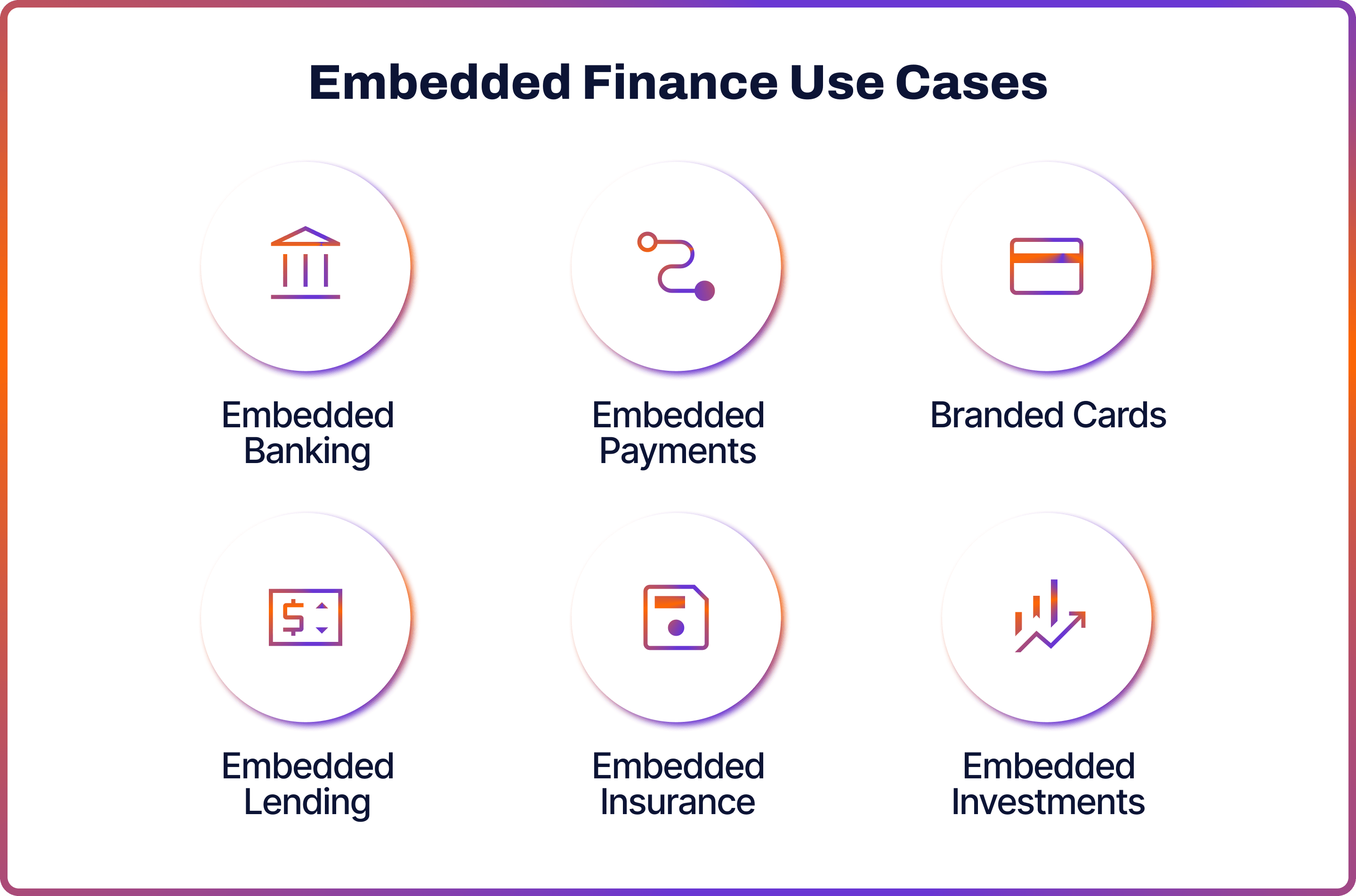
Embedded Banking
Embedded banking allows non-financial companies to offer banking accounts for their clients. An example of successful embedded banking is Uber, the ride-sharing and food delivery company, which integrated various financial services for both drivers and customers.
Uber Cash lets users add funds to their Uber account for rides and Uber Eats. Additionally, they launched Uber Money, a division focused on providing financial products to their drivers, including a mobile bank account and an Uber Pro Card.
Embedded Payments
Eliminating the struggle of manually entering credit card details can reduce the likelihood of cart abandonment. Embedded payments streamline this by securely linking and storing payment methods for future use with just a single click.
A prime example is the Starbucks app, which retains users' credit or debit card information, enabling effortless payments. This is coupled with the benefit of earning reward points each time the app is used for transactions.
Branded Cards
Branded credit cards have long been a staple. Department stores offered them long before, think of an M&S Credit Card. Embedded finance, however, broadened the scope, enabling more companies to offer these cards and diversifying their use cases.
Embedded lending
Embedded lending provides loan options directly at the point of sale. Previously, consumers relied on credit cards or standard loans from banks. This new approach broadens access to lending for consumers and boosts sales for companies.
The key embedded finance companies that specialise in lending are the Buy Now Pay Later (BNLP) providers such as Klarna, Affirm and Afterpay. They allow customers to split payments up over time at the online checkout process.
Embedded investing
Embedded investing enables non-financial platforms to integrate investment services. This allows users to invest directly within their platforms. Previously, investing services were monopolised by big traditional institutions such as Fidelity and Goldman Sachs.
An example of embedded investing is Revolut. Originally a digital banking app, Revolut has integrated investing services into its platform, enabling users to buy and sell assets within the app.
Embedded insurance
Embedded insurance simplifies buying insurance by making it available at the point of sale. This approach provides insurance exactly when and where it's needed, eliminating the need for separate dealings with an insurer or agent. Often, it even presents multiple options for competitive coverage.
Companies integrate digital insurance through partnerships with fintech firms. These fintechs weave insurance choices into the checkout process, allowing consumers to easily add insurance to their purchases as an extra option.
For example, when purchasing furniture in IKEA, customers can buy IKEA’s own insurance for their items. Or, Apple customers can add AppleCare as an add-on when buying a device.
Benefits of Embedded Finance
- Customer Experience: Embedded finance products integrate financial services into familiar platforms, enhancing the user experience. Customers enjoy the convenience of accessing services like payments, lending, or insurance within a single platform or app.
- Financial Inclusion: By embedding financial services in commonly used platforms, they become accessible to more people, including those who might not have easy access to traditional banking.
- Innovation in Financial Products: Embedded finance encourages the invention of better financial products. This leads to personalised and efficient embedded finance solutions.
- Operational Efficiency: Businesses benefit from streamlined operations as integration with embedded finance reduces the need for separate systems. This efficiency can lead to cost savings and improved management.
Embedded Finance Trends & Forecasts
Embedded finance is likely to keep the momentum, with the key trend being strong sector growth. The Global Embedded Finance Market size is expected to reach $384.8 billion by 2029, rising at a market growth of 30.0% CAGR during the forecast period.
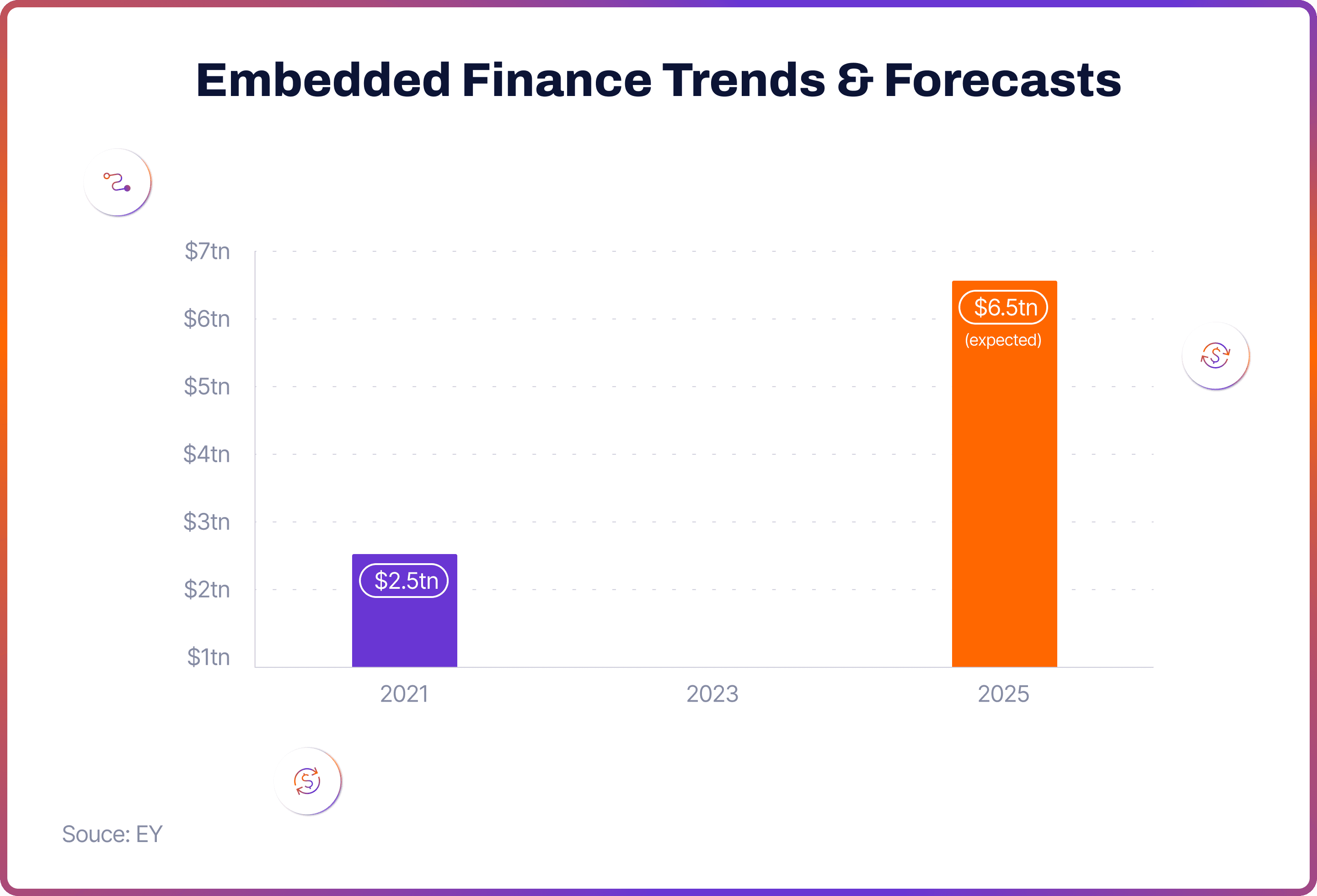
According to another research by EY, the volume of payments through embedded channels reached $2.5tn in 2021, and is expected to surge to $6.5tn by 2025.
OpenPayd, a BaaS provider, estimated the embedded finance market to be worth $7.2tn by 2030, with over 92% of businesses planning to roll it out within five years. Oracle’s research echoed this sentiment, estimating that the value of embedded finance market will exceed $7 trillion in the next 10 years.
A Juniper Research study conducted in November 2022, expected the revenue from embedded finance to exceed $183bn in 2027, rising from $65bn in 2022.
Open Banking & Payments with Noda
Elevate your business with Noda’s payments and open banking solution. Our all-in-one platform prioritises customer understanding, efficient operations, and growth.
Noda is a worldwide payment and open banking provider for seamless business transactions. From payment facilitation to financial analytics, Noda has got you covered. Our platform uses cutting-edge AI and machine-learning technologies. Your payments are our priority.
FAQs
What is embedded finance used for?
Embedded finance has a wide variety of use cases. For example, it can be used as a banking service embedded into a retailer’s platform or an embedded lending option, such as via Klarna, at the point of sale. The space is highly innovative, and companies constantly develop new solutions.
What are embedded payments?
Embedded payments are a way of integrating payment methods directly into various digital platforms or services. This means that when a customer uses an app or website, they can pay for things right there, without having to leave the platform. A prime example is the Starbucks app, which retains users' credit or debit card information, enabling effortless payments.
How can businesses implement embedded finance?
Businesses that want to integrate embedded finance should first determine what service they’d like to embed. This can vary from banking and payments to lending, insurance, and investments. Businesses should then choose a trusted embedded finance provider to help with the integration.
What are the benefits of embedded finance?
Benefits of embedded finance include better user experience, higher sales and operational efficiency, increased innovation and financial inclusion.
What’s the future of embedded finance?
The forecasts mentioned in this article promise a bright future for embedded finance. According to another research by EY, the volume of payments through embedded channels reached $2.5tn in 2021 and is expected to surge to $6.5tn by 2025.
Latest from Noda
Digital Payment Trends: Navigating the Future

Payment Methods in Ireland in 2026: Everything You Need to Know

Top Payment Methods in Austria: How to Accept Payments Efficiently in 2026

