In the ever-changing landscape of global finance, open banking is emerging as a powerful catalyst transforming how businesses and consumers interact with financial information. Notably, the US and Europe, both prominent players in the financial arena, provide intriguing case studies on the different approaches to open banking.
Here we shed light on the differences between the two markets and offer a comprehensive understanding of how open banking has evolved in the two regions.
Regulation of Open Banking: EU vs USA
Arguably the biggest difference between open banking in the USA and Europe is how they regulate the space. While Europe is pioneering in a regulatory-driven approach, on the other side of the Atlantic, an industry-led strategy is preferred.
Europe’s Open Banking Regulation: PSD2 & PSD3
Europe has been a pioneer in open banking regulation, thanks to the revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2) implemented in 2018. This directive has played a crucial role in the developing open banking in Europe. Its purpose is to dismantle the monopoly banks traditionally had over customer data by requiring them, with explicit customer consent, to share this data with third-party providers. This approach democratises financial data and has spurred innovation and competition within the European financial sector.
Unlike fragmented approaches seen elsewhere, PSD2 provides a standardised framework for open banking across EU member states. Each country integrates the directive into its national law, ensuring a harmonised approach to open banking throughout Europe. For example, in the UK, the Open Banking Standard was adopted to comply with European regulation, or in Germany, where The Berlin Group (TBG) introduced NextGenPSD2, a comprehensive framework for open banking.
In July 2023, Europe made further progress in open banking with the introduction of PSD3, building upon the foundation established by PSD2. The European Commission's goal with PSD3 is to further enhance API sharing.
CFPB’s Initiative to Regulate Open Banking in the US
Despite the US open banking strategy focussed on industry rather than regulation, the tides are also beginning to turn towards regulatory change on the other side of the Atlantic.
In June 2023, Rohit Chopra, the director of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), revealed plans for upcoming open banking regulations. These new rules, based on Section 1033 of the Dodd-Frank Act, seek to promote competition among financial service providers in the US.
Chopra envisions a future where institutions are required to give consumers the ability to share their financial data with fintech companies, other banks, or online lenders. The regulations are expected to be finalised by 2024.
Open Banking Adoption in Europe versus the US
The adoption of open banking between the European and US markets is at different stages, reflecting the strategies of the two regions.
Open Banking Adoption in Europe
The EU’s open banking journey has been a carefully planned and systematic process. Over the past few years, there have been regulatory requirements, extensive media coverage, and industry conversations surrounding this approach to finance.
Consequently, European adoption rates of open banking are soaring. In January 2022, there were approximately 5 million active users of open banking in the UK, according to a report by OBIE. Considering that the country’s total population with any type of bank account is around 47 million, this means that about 10.6% of the country's banked population is utilising open banking services. The UK is considered one of the leaders in open banking in Europe, followed closely by Germany.
Although there is no official data on the number of open banking users in Europe, Sifted reported that according to Nordigen CEO Rolands Mesters, only around 5-7% of Europeans have utilised open banking. The adoption rate varies not just due of regulatory disparities but also because of cultural attitudes towards payment methods.
In 2019, a Forrester Research report revealed that 34% of European adults used mobile applications or bank websites for their banking needs. Additionally, it projected that 64% of adults will adopt open banking in the near future.
Open Banking Adoption in the US
While Europe has implemented strict regulatory mandates, the industry-driven efforts are fueling the growth of open banking in the US. According to a report by Deloitte Insights published in 2019, one in five US consumers saw value in open banking, with higher interest observed among millennials and Gen Z. Hence it may be crucial for American banks to focus their initial open banking initiatives on younger generations.
Nevertheless, consumers expressed concerns about privacy, security, and the use of personal data, which should not be overlooked. This emphasises the importance for banks to educate consumers about the advantages of open banking. Interestingly, less than one-third of consumers felt they had control over their financial data.
Meanwhile, a survey conducted by Mastercard in 2021 revealed that 81% of US adults were connecting their bank accounts to third-party applications. This widespread adoption of banking highlights its increasing popularity among US consumers.
Future of Open Banking in Europe vs the US
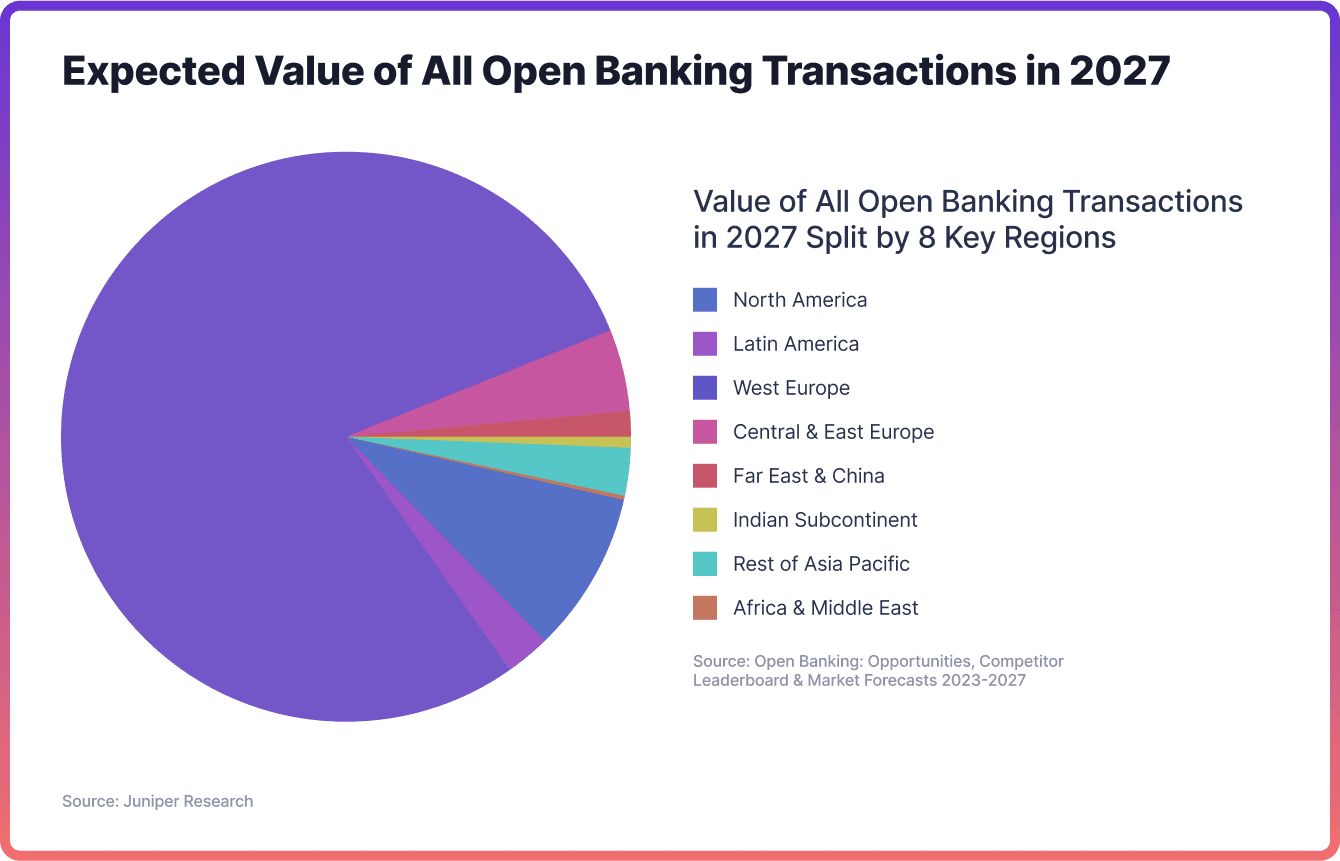
Open banking is expected to experience significant growth, with global payment transactions estimated to increase from $57 billion in 2023 to over $330 billion by 2027, according to Juniper Research. Western Europe is expected to significantly lead the way, followed by North America and Eastern Europe. The surge can be attributed to the rise of new use cases, which provide a simpler and more efficient alternative compared to traditional methods like card payments.
As open banking continues to advance, finding the right balance between convenience and security becomes crucial for its future. This holds for Europe and the US as they navigate the evolving landscape of financial services.
Key Differences in Open Banking in Europe vs US
- Approach: Europe's path towards open banking has been carefully navigated, largely guided by regulatory requirements such as PSD2. On the other hand, the US has taken a more organic approach, allowing industry leaders to take the lead in identifying and filling gaps in the financial sector, often before regulations catch up.
- Regulation: In Europe, the open banking ecosystem is tightly regulated by the PSD2 standard. This ensures a unified vision and direction for the technology's development across member states. On the other hand, the US takes a more hands-off approach, operating in a market-driven environment with minimal regulatory oversight. Yet the upcoming CPFB initiative may change the strategy.
- Adoption: The significant contrast in adoption rates between Europe (5 million users) and the US (80 million users) is not a mere numerical difference. It reflects the wider range of functionalities and more enticing applications available in the US, catering to diverse consumer needs.
- Security: Conversely, the US approach to open finance has raised concerns about security. Some American fintech companies access accounts through screen scraping techniques to gather data. While this practice is widely accepted in the US, it is inherently less secure compared to European methods of compulsory API data sharing. In the US, users often encounter bank login interfaces on third-party platforms that resemble phishing attempts. Despite the security implications, this approach has been widely adopted with little resistance from regulators or banks.
Final Thoughts
Open banking is a transformative force in the global finance landscape. It combines innovation, consumer empowerment, and regulatory foresight to democratise financial data. While Europe and the US follow different paths, both regions strive for the same goal of making financial information accessible to all.
The future of open banking holds great promise as adoption rates rise and new technologies emerge. However, its success relies on finding the right balance between innovation and trust. Moving forward, it is crucial for industry stakeholders, regulators, and consumers to work together in shaping an open banking environment that is not only technologically advanced but also secure and transparent.
Latest from Noda

Top Payment Methods in Austria: How to Accept Payments Efficiently in 2026

GoCardless Review 2026: What Merchants Need to Know

AIS vs PIS in Open Banking: What’s the Difference & When to Use Each

