The United Kingdom has emerged as a leading force in the world of open banking infrastructure. As of 2025, Brits have successfully embraced this ground-breaking concept, reshaping the financial landscape and presenting a regulatory framework to help businesses navigate new possibilities.
In this article, we provide an overview of the UK’s open banking, from the formation of the law surrounding it to its current state and emerging trends.
What Is Open Banking?
Open banking is a modern, efficient approach to handling finances and making direct payments, without added fees. Open banking introduces user-friendly payment alternatives such as direct bank transfers, real-time payments, and custom financing options. The result? Greater payment flexibility for customers, along with a smoother and more efficient checkout experience.
With services like Noda, merchants can, with customer consent, access key banking details. This insight helps accept instant bank payments from customers, as well as understand their customers behaviours, credit profiles, and preferences, allowing for more tailored offerings.
Open banking also enables both individuals and businesses to share bank account information and initiate payments through secure Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). These APIs act as secure connectors between banks, merchants, and financial service providers, enabling seamless data exchange.
History of Open Banking in the UK
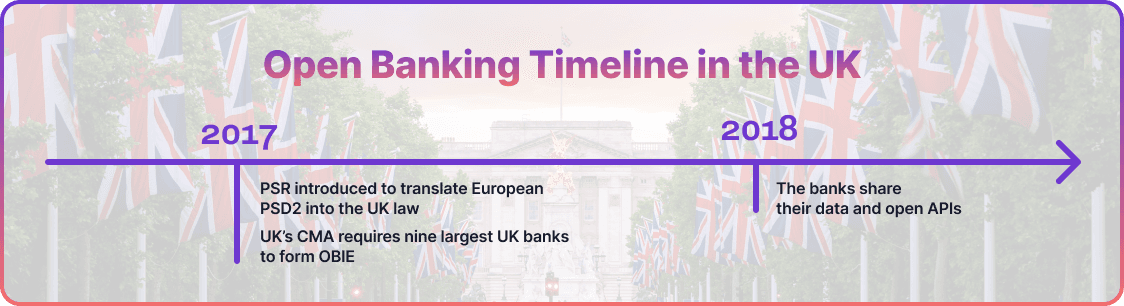
The UK's open banking initiative originated from the wider European push for financial transparency and empowering consumers. This journey began in 2017 with the introduction of the Payment Services Regulations (PSRs). Serving as the legislative framework, these regulations translated the revised European Directive, the Payment Services Directive (PSD2), into UK law, marking the official start of open banking in the country.
Following its investigation into retail banking, the UK’s Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) made it mandatory for the nine largest UK banks, collectively referred to as the CMA9, along with a selection of other financial institutions, to implement open APIs. This requirement enabled authorised third-party providers (TPPs) to access customer-permitted data.
The nine banks established the Open Banking Implementation Entity (OBIE) in 2017. Its main objective has been to promote competition and establish a standardised open banking framework that enables convenient, secure account access. As of 2025, OBIE has successfully onboarded over 145 regulated TPPs and facilitated more than 12 million active users of open banking services in the UK, making it one of the most mature ecosystems globally.
Open Banking Regulation in the UK
Open banking in the UK is regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and the Payment Systems Regulator (PSR), which oversee compliance for banks, building societies, and third-party providers (TPPs). Their joint supervision ensures that all participants meet UK standards for security, consumer protection, and operational integrity.
The Open Banking Implementation Entity (OBIE) continues to manage the UK Open Banking Standard, which includes:
- Open Banking API standard: Featuring up-to-date technical documentation (Read/Write APIs, Open Data APIs, Directories, Dynamic Client Registration, and MI reporting) aligned with both PSD2 and evolving UK requirements.
- Security profiles: Developed alongside the OpenID Foundation, covering TPP onboarding, redirect flows, decoupled authorization, and secure API access.
- Customer experience guidelines: Based on extensive user testing and regulatory input, these standards streamline consent flows and reduce friction in compliance with PSD2.
- Operational guidance: Ensures that banks and TPPs meet their obligations regarding API performance, incident management, testing, and supervisory MI submission.
- Certification services: Provide a compliance pathway for banks and TPPs, enabling exemptions in contingency mechanisms once certified.
These frameworks support a thriving ecosystem: as of March 2025, the UK boasts 13.3 million active open banking users, with 31 million open banking payments per month, representing roughly 8% of all Faster Payments. Initiatives like variable recurring payments (VRPs), which now account for nearly 13% of open banking transactions, are also gaining traction backed by regulators.
Together, the FCA, PSR, and OBIE form a robust structure supporting ongoing innovation across UK open banking, including the shift toward a future Open Finance and enhanced resilience under the upcoming Data (Use and Access) Bill and DORA frameworks.
Open Banking Trends in the UK
Open banking in the UK is on a significant rise. Adoption rates have surged, and the ecosystem of third-party providers (TPPs) is expanding rapidly.
With 13.3 users in March 2025, and this remarkable growth represents a significant increase from 3 million users in June 2022, up from just 1 million in January 2020.
The growth is not restricted to user numbers alone. The realm of open banking services, available to both consumers and businesses, has expanded significantly. These services encompass a wide array, from Account Information Services (AIS), which offer real-time, consolidated financial insights, to Payment Initiation Services (PIS), that facilitate secure and frictionless direct bank payments.
Small businesses are benefitting greatly from the implementation of open banking. The Impact Report 7 highlights several key outcomes:
- 18.4%/1 in 5 small businesses reported improved decision-making through open banking services
- 82% experienced enhanced business efficiency
- 52% saw a reduction in internal costs, and 61% noted lower external costs
- 77% reported being better able to manage late payments and pursue unpaid invoices
When it comes to adoption across different business sizes, a clear trend continues: larger small businesses (those with 10–49 employees) are more likely to utilise these services. However, smaller micro-businesses are also steadily increasing their adoption rates, showing that the advantages of open banking are recognised across the entire business spectrum.
Consumer adoption is also climbing steadily. As of late 2023, 17% of digitally enabled UK consumers were actively using at least one open banking-powered product or service, up from approximately 11% in March 2022 and 6–7% in March 2021. In May 2025 there were 13.56 mln open banking users in the UK, including 1.1 new users.
This continued momentum signals not only the growing maturity of open banking in the UK but also its mainstream integration into everyday financial behaviour for individuals and businesses alike.

Future of open banking in the UK
The future of open banking in the UK holds great promise and abundant opportunities. According to the Open Banking Limited’s report, the implementation of the Open Banking Standard has continued to play a pivotal role in driving a fintech renaissance.
The report emphasised the significance of sustained oversight and coordinated governance to ensure positive outcomes for end users in open banking. It highlighted the ongoing need for the UK’s Open Banking Standard to evolve in line with market shifts and the changing expectations of stakeholders and consumers.
According to the report, a central responsibility of the future steward of the Standard will be to prevent fragmentation within the open banking ecosystem and discourage the growth of unregulated or inconsistent functionalities.
Stakeholders from across the industry have reiterated the need for widespread and uniform adoption of the UK Open Banking Standard. This includes consistent implementation of not only the technical API specifications, Customer Experience Guidelines, and operational performance metrics, but also extending these frameworks across all UK banks.
According to OBL’s impact report, 13.3 million active users are now using open banking in the UK alone, with 31 million payments processed monthly, indicating steady regional growth.
On the global stage, OBL notes that expanding API utilisation, VRP adoption, and increasing fintech integrations are visible across Europe and North America, suggesting that the more conservative forecasts (such as those from Juniper and Accenture) have likely been exceeded.
Final Thoughts
Open banking in the UK has made significant progress since its inception. It has revolutionised the financial landscape by empowering consumers with greater control over their financial data and sparking innovation in the fintech industry.
However, this journey is still ongoing. As the open banking ecosystem continues to evolve, it is crucial to ensure alignment with broader initiatives, maintain high standards of reliability and customer experience, and uphold value for all sectors of society, including vulnerable customers.
Expand to the UK with Noda
The UK is ripe for open banking-powered e-commerce: over 13 million Brits use open banking solutions and demand faster, seamless payment methods is higher than ever.
Why choose us for the UK:
- Comprehensive bank coverage
Connect to all major UK banks (Barclays, HSBC, Lloyds, NatWest, Santander, plus challengers like Monzo, Starling, Revolut) and access 2,000+ banks across Europe via a single integration. - Extremely low fees
Keep margins healthy with transaction costs starting from 0.1%, giving UK merchants a compelling pricing advantage. - Instant settlement
Funds arrive in merchant accounts within seconds over Faster Payments - no card networks, no delays. - Effortless integration
Go live in minutes using plugins for WooCommerce, Magento, Prestashop, OpenCart — or integrate directly via our REST API. - Multi-rail payment support
Seamlessly blend open banking, card payments, Apple Pay, and Google Pay in one unified checkout for maximum flexibility. - No-code payment solutions
Instantly generate payment links and QR codes, accept bank payments without writing a single line of code. - Dedicated local support
Benefit from a UK-based account manager during onboarding and beyond, ensuring smooth setup and ongoing assistance.
Contact Noda for a no-obligation demo. Our open banking experts will be happy to look into your unique business case.
FAQs
Does the UK have open banking?
Yes, the UK has a fully implemented open banking framework launched in 2018, supported by major banks and regulated third-party providers.
Which UK banks offer open banking?
The nine largest UK banks, the 'CMA9', are mandated to offer open banking, with other banks also offering APIs. These include Barclays, Lloyds Banking Group, Santander, Danske, HSBC, RBS, Bank of Ireland, Nationwide, and AIBG.
Is open banking legal in the UK?
Yes, open banking is legal in the UK. It is regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and the Open Banking Implementation Entity (OBIE), which ensures compliance with the regulations and the protection of consumers' data.
Is open banking safe in the UK?
Yes, open banking in the UK is highly secure, regulated by the FCA, and protected by strong customer authentication and data privacy laws.
Latest from Noda

Top Payment Methods in Austria: How to Accept Payments Efficiently in 2026

GoCardless Review 2026: What Merchants Need to Know

AIS vs PIS in Open Banking: What’s the Difference & When to Use Each

