Open banking and open finance emerged as game changers in the ever-changing financial landscape. These ground-breaking ideas aim to transform how we handle our finances, providing unprecedented control and convenience.
Yet while the two concepts sound alike, there are key distinctions between them. Here we take a look at the key mechanisms, similarities and differences of open finance vs open banking, to demystify the two concepts.
What is Open Banking?
Open banking revolutionised the financial sector, granting customers complete control over their financial data. This practice involves the secure sharing of information between financial institutions and authorised third-party service providers through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), always with the customer's consent.
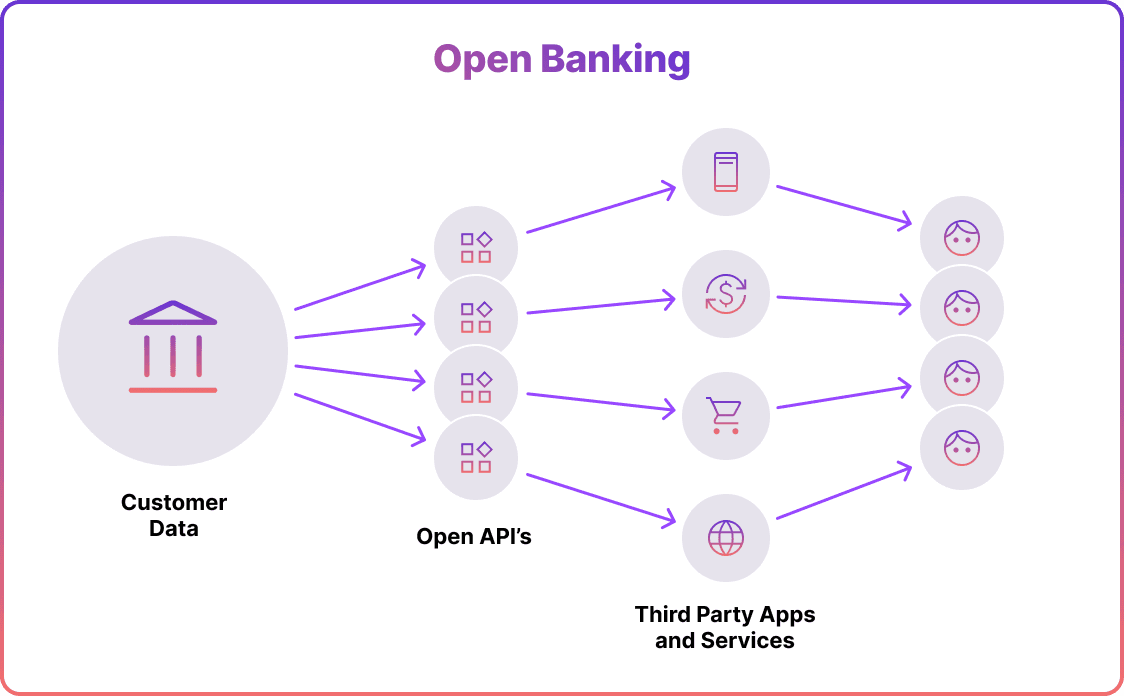
Its primary objectives are to enhance transparency, encourage healthy competition, and empower individuals by offering improved access to and management of their financial information.
Open banking has sparked innovation, enhancing the customer experience and helping companies cut down on payment expenses. It allowed third-party providers to access customer information and facilitate transactions. As a result, an array of financial services and products have emerged, including inventive credit models and the automation of corporate finance management.
As a global phenomenon, open banking is being adopted by banks and fintech companies around the world. In the UK, for instance, 10-11% of digitally-enabled consumers were estimated to actively use at least one open banking service as of June 2022. The percentage rose from 6-7% in March 2021.
Research conducted by Accenture in 2021 revealed that 76% of banks globally anticipated a significant increase of 50% or more in customer adoption and usage of Open Banking APIs between 2024 and 2026.
Furthermore, the market was projected to reach a staggering $43.15 billion by 2026, with a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 24% during the next five years.
What is Open Finance?
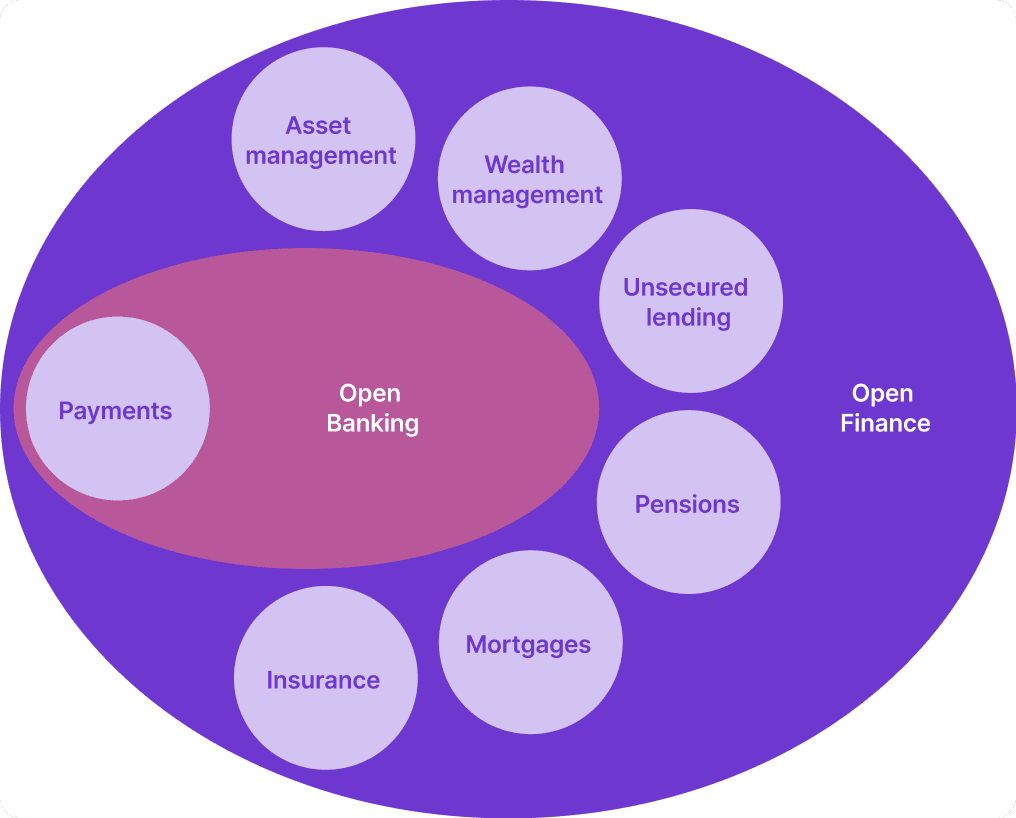
Open finance represents the next step in the development of open banking, bringing its core principles to a wider range of financial products.
While open banking primarily emphasises payment accounts, open finance embraces a broader array of financial offerings and services. These include savings accounts, investments, pensions, mortgages, insurance, and more.
Open finance operates at a larger scale compared to open banking. This allows authorised third-party service providers to access a wider range of customer data, which can then be utilised to create financial products and services that are more personalised and intuitive. Consequently, consumers gain a more comprehensive understanding of their financial well-being.
Key Similarities and Differences
Open banking and open finance have a shared objective - empowering consumers with greater control over their financial data. Both concepts operate under the guiding principle that individuals should determine who has access to their information and the authority to make payments on their behalf.
However, there are key differences between open banking and open finance.
Scope
Open banking primarily focuses on payment accounts, while open finance goes beyond. It encompasses a broader array of financial products, including savings accounts, investments, pensions, mortgages, and insurance.
Regulatory framework
Open banking has emerged as a regulatory initiative in Europe through the Revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2). This directive mandated financial institutions to share payment account data with regulated third-party providers, with the customer's consent. The regulation is specific and limited to payment accounts.
Meanwhile, open finance’s regulatory framework is still in progress. The goal is to extend the principles of open banking to a broader range of financial products and present consumers with a more comprehensive understanding of their financial situation. However, specific regulations for open finance are still being defined and may vary across different regions.
Benefits of Open Banking and Open Finance
Open Banking and Open Finance offer numerous benefits to consumers, businesses, and the financial industry as a whole. Let's explore some of the key advantages.
For consumers
- Data control: Open banking and open finance give consumers greater control over their financial data. This empowers individuals to determine who can access their information and for what purpose, putting them firmly in the driver's seat.
- Financial management: When consumers consolidate information from various accounts and financial products, they gain a comprehensive view of their financial situation. This holistic approach facilitates improved financial management and decision-making.
- Personalised services: Financial service providers can offer personalised and tailored financial products and services by leveraging a wider range of financial data. This includes customised interest rates for loans and investment advice that aligns with individual financial goals.
- Increased competition: Open banking and open finance foster increased competition among financial service providers. This heightened level of competition has the potential to deliver several benefits to customers, including improved customer service, reduced fees, and a more comprehensive range of innovative products.
For businesses
- Access to financial data: Open banking and finance offer businesses the opportunity to tap into a vast pool of valuable customer information with their consent. This invaluable resource equips them with a profound understanding of their clientele, allowing for tailored offerings and superior service provision.
- Financial operations: Open banking has the potential to optimise business processes. They can automate accounting tasks, accelerate payment processing, and simplify lending procedures.
- Innovation: In the open data environment, businesses have abundant opportunities to innovate and create new financial products and services. This leads to growth and enhances competitiveness.
Future of Open Banking & Open Finance
The future of open banking and open finance shows immense promise and has the potential to revolutionise the financial sector. These concepts are continuously evolving, leading to greater accessibility to financial services, driving innovation, and enriching customer experiences.
Open banking, an already transformative force, will continue to evolve and mature. This will result in more financial institutions and third-party providers leveraging its potential. As a result, we can expect an increase in the number and diversity of services being offered. These services will range from sophisticated account aggregation to advanced predictive analytics and personalised financial advice.
Open finance is poised to build upon the foundations of open banking, offering a broader range of financial products that enhance consumer and business control over their economic lives. By extending the benefits of data sharing, open finance can empower individuals and businesses with greater visibility and autonomy. Moreover, as the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, it needs to ensure both the expansion of these concepts and the protection of consumer data.
Final Thoughts
Open banking and open finance are transforming the financial landscape, giving individuals more control over their financial information while driving innovation in the industry. As these concepts continue to develop, they offer businesses new opportunities and consumers personalised and comprehensive financial services.
Although regulatory aspects are still being defined, particularly for open finance, it is undeniable that momentum is building. Moving towards a future of open data, these principles will play a crucial role in shaping this era of data-driven services, revolutionising how consumers and businesses manage their finances.
FAQs
What is the main difference between open banking and open finance?
The main difference between open banking and open finance lies in their scope. Open banking primarily focuses on payment accounts, allowing third-party providers to access this data with the customer's consent. On the other hand, open finance extends this principle to a broader range of financial products and services, including savings accounts, investments, pensions, mortgages, and insurance.
What is the role of open finance?
The role of open finance is to extend the principles of open banking to a wider array of financial products. This allows authorised third-party service providers to access a more extensive customer data, which can then be used to create more personalised and intuitive financial products and services. It gives consumers a more holistic view of their financial health and fosters innovation in the financial sector.
Latest from Noda

Top Payment Methods in Austria: How to Accept Payments Efficiently in 2026

GoCardless Review 2026: What Merchants Need to Know

AIS vs PIS in Open Banking: What’s the Difference & When to Use Each


