The world of banking is on the cusp of a monumental shift, one that holds the potential to revolutionise the way businesses interact with financial services. Traditional banking, once the unchallenged cornerstone of commerce, is now having to share the stage with a vibrant and tech-driven newcomer: open banking.
The value of open banking transactions worldwide reached $56bn in 2023, and is expected to rise sharply. Understanding the ins and outs of the open banking vs traditional banking debate is more than just knowledge—it's a competitive edge. Whether you're a startup founder seeking smarter ways to manage finances, or an established business owner looking for the next big opportunity, it’s time to turn the page on the future of banking.
What is Open Banking?
At its core, open banking is a modern approach to banking that breaks away from the confines of the systems used by traditional banks, instead embracing the boundless possibilities of the digital world. But what exactly is open banking and payments, and how does it work?
Power of APIs
Open banks hinge on the use of open APIs—Application Programming Interfaces. These are essentially bridges that allow different software systems to communicate and share information with each other seamlessly. Imagine it as a kind of universal translator, converting jargon from one software into a language another software understands.
These open APIs enable third-party developers to build applications and services around the financial institution. This means you can have access to a host of services from different providers, all interconnected and all under one digital roof. The result? An easier way to manage money, compare products, make payments, and integrate financial services into your business operations.
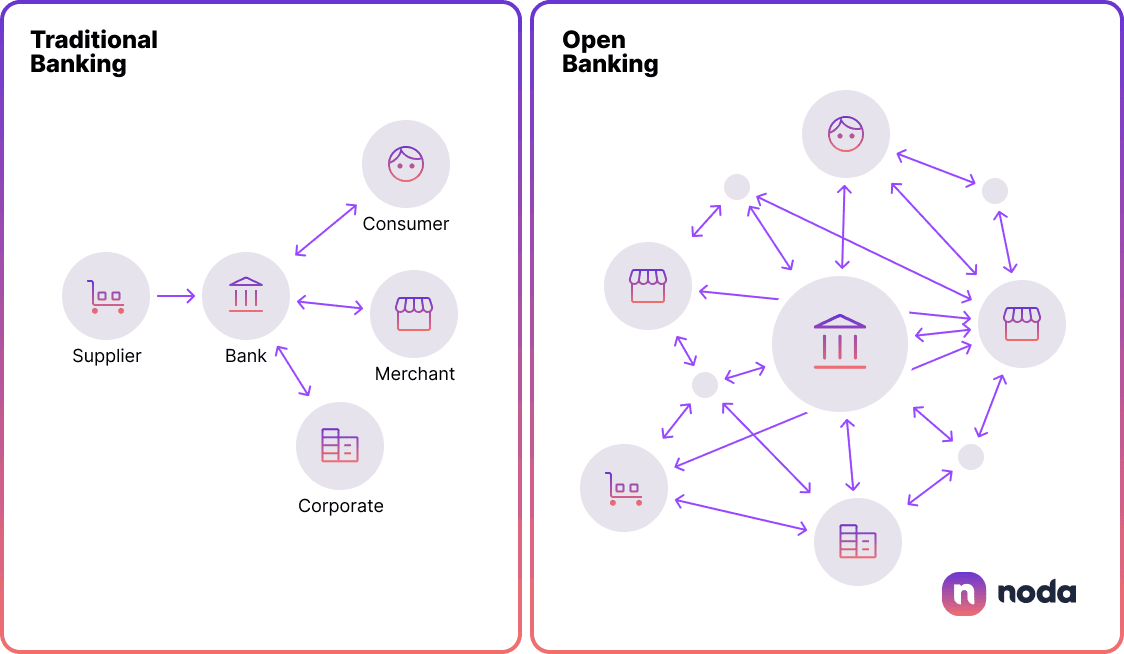
Open Banking vs Traditional Banking
Although at the core of both is providing financial services for clients, there are fundamental differences between open banking vs closed banking.
Open banking | Traditional banking | |
| Data ownership | Users have control over their data | Banks have control over customer data |
| Data sharing | Enabled via APIs with third parties | Data is typically not shared |
| Product offering | Personalised financial services | Standardised services |
| Innovation | Encourages innovation | May be limited due to internal bureaucracy |
| Collaboration | Collaboration with fintechs and other players | Minimal or zero collaboration |
| Competition | Encourages competition | Maintains higher barriers to entry |
| Service delivery speed | Faster due to API integration | May be slower due to internal processes |
| Regulation | Regulated for data sharing | Complies with traditional regulations |
- Data ownership: Open banking shifts the control of data back to users, who decide who to share it with. But in the world of closed banking, banks hold all the cards, executing exclusive control over customer data.
- Data sharing: In open banking, APIs act like matchmakers, connecting and sharing customer data securely with approved third parties. Closed banking? It's more of a vault, locking away data with no sharing mechanisms.
- Personalise products: Open banking brings personalisation front and centre, crafting financial products and services that fit each customer like a glove. In contrast, closed banking has a 'one-size-fits-all' approach which might not always be the best fit.
- Innovation: Open banking promotes innovation, inviting third-party developers to create novel services. Closed banking, however, often finds itself tangled in its own bureaucracy, slowing down the pace of advancement.
- Collaboration: Open banking promotes a spirit of collaboration between banks, fintechs, and other players. In the realm of closed banking, it's more of a solo journey, with little interaction with outsiders.
- Competition: Open banking opens the gateway for competition, allowing fintechs and other newcomers to join the space. Closed banking maintains high barriers to entry, restricting it to the financial services arena.
- Speedy service delivery: Open banking operates in the fast lane, with APIs powering quick development and delivery of services. Closed banking, on the other hand, can be slower due to internal development and approval processes.
- Regulation: Although both must comply with relevant regulation, open banking steps to the tune of regulations like the EU's PSD2, which encourage data sharing with customer consent. Closed banking, on the other hand, follows the traditional banking regulation.
Why Choose Open Banking over Traditional Banks?
As we delve deeper into the subject, it becomes clear why open banking holds such a strong appeal for businesses and consumers alike; and why traditional banks may be challenged.
Personalised Banking Services
In the past valuable consumer financial data has lain dormant within the traditional banks' systems. This under-utilisation resulted in the provision of services that often missed the mark in meeting individual needs.
Open banking changes this by empowering its clients to share their data willingly. In return, they receive tailor-made financial services, better attuned to their unique needs, thus enhancing their banking experience.
Accelerating Transactions
In the business world, time is a crucial commodity, and open banking appreciates this fact. Enabled by the integration of APIs, open banking can significantly expedite transaction times.
This capability facilitates direct open banking payment initiation from an account, bypassing the slower traditional payment networks. The result is not just faster, but also more efficient financial operations, crucial in today's fast-paced environment.
For entrepreneurs and businesses, this could translate into better cash flow management, quicker customer transactions, and enhanced operational efficiency. Thus, open banking offers a faster and more streamlined banking experience versus other payment methods.
Boosting Innovation
The banking sector is no longer just vying with fellow banks. Competition now comes from tech companies ready to serve up innovative services at a pace that traditional banks struggle to match.
Open banking, facilitated by the sharing of banking APIs, allows for a quick, collaborative approach to innovation. It enables banks to tap into user data insights, work alongside other financial institutions, fintech startups, and approved third-party service providers.
This partnership can speed up the development and integration of new products and services, ensuring a faster route to market and fostering an open banking environment primed for innovation.
Future of Banking
Looking ahead, it's clear that open banking is gaining momentum over the traditional banks in the sector's future. According to Allied Market Research, the global open banking market is expected to grow to an impressive $123.7bn by 2031, while Future Market Insights predicts a market worth $158.6bn by 2032.
This is, of course, not equivalent to the size of traditional banking, which is in tens of trillions. Yet the growth of the innovative sector is accelerating, especially with the rise in consumer adoption. It's now estimated that at least 10–11% of digitally-enabled consumers are active users of at least one open banking service.
This growing preference indicates a major shift towards open banking, signalling its integral role in shaping the future of financial services. Given these trends, the future of banking appears to be not just open, but expansively innovative, competitive, and consumer-focused.
Final Thoughts
Traditional banking, once the sole powerhouse of the financial world, is now sharing the spotlight with the fresh, technology-fuelled approach. Through the use of open APIs, open banking fosters connectivity, allowing various software systems to interact seamlessly.
The open banking architecture allows for a more competitive, diverse ecosystem that ultimately benefits the consumer.
All these changes underscore the importance for businesses to understand the distinction between traditional and open banking. Embracing open banking isn't merely about staying on trend; it's about preparing for the future of financial services.
Latest from Noda
Digital Payment Trends: Navigating the Future

Payment Methods in Ireland in 2026: Everything You Need to Know

Top Payment Methods in Austria: How to Accept Payments Efficiently in 2026


