Open data is an ongoing topic of discussion in both the public and private sectors. With initiatives like open banking in place in the EU, the focus now shifts to the broader open data economy.
In this article, we’re looking at what this economy could look like, its potential benefits for various industries, and future trends. We will discuss the opportunities open data presents for innovation and growth across sectors.
What Is an Open Data Economy?
An open data economy is where data is openly accessible to everyone for use and sharing without any limitations. This would allow governments, companies, and individuals to leverage open data for societal, economic, and environmental benefits.
In an open data economy, data must be shared with a license in formats that are standardised and readable. This paradigm is built on the concept of data transparency and the belief that data should be a public good, fostering innovation and cooperation across different areas.
From Open Banking to Open Data
Open banking applies the principle of data transparency to the banking industry, in other words, opening banking data. It's a system embraced in the UK and EU through the PSD2 regulation, which mandated banks to share customer data with authorised fintech firms. This process is strictly regulated and requires the explicit consent of the customer.
Open banking operates on Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), which are sets of rules allowing different software systems to interact. As a digital intermediary, APIs facilitate communication between banks and fintech companies.
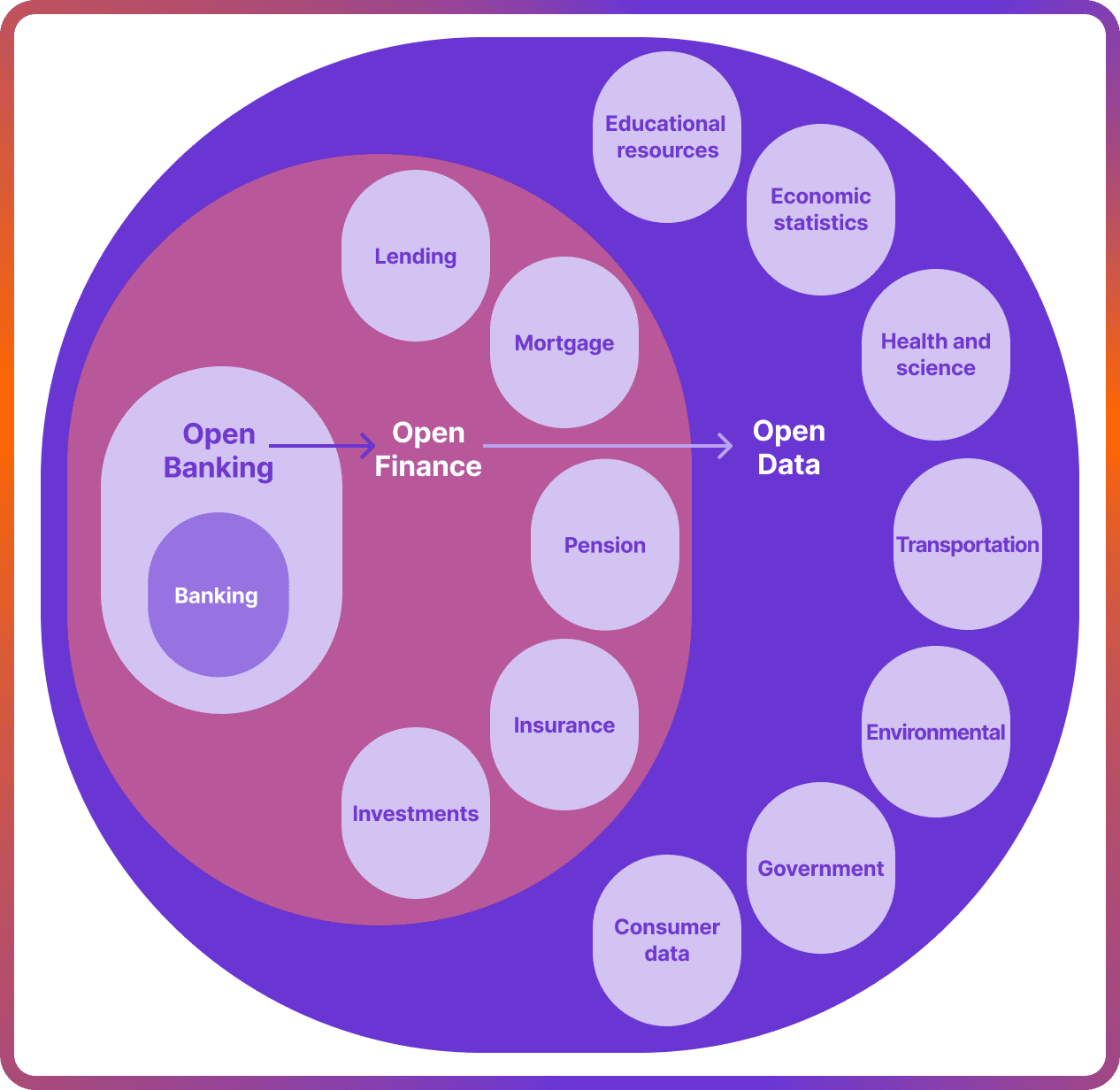
Open finance represents an evolution of applying the concept of open data in finance. In open finance, data is shared among a wider array of financial sectors, including:
- Banking data
- Investment data
- Insurance data
- Pension data
- Mortgage data
- Lending data
While open finance principles are not widely adopted worldwide, Brazil is one of the few pioneers. The country started the final phase of its implementation in March 2022.
The open data economy expands transparency beyond finance, sharing a wide range of information. This can include:
- Government and public sector information
- Environmental and climate data
- Transportation and infrastructure details
- Health and scientific research data
- Financial and economic statistics
- Educational resources
- Consumer data across sectors
Open Data in Europe
The European Union (EU) leads in promoting the open data project, with several laws supporting its principles:
- Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2): In 2018, PSD2 required banks to share customer data with approved third parties, with the customer's consent. This regulation paved the way for open banking.
- Open Data Directive: Effective from 2019, the regulation mandated broader access to and re-use of data from the public sector across EU nations. This covers information from government entities, local governments, and legally established organisations.
- Data Governance Act & The Data Act: Published in 2022 and 2024 respectively, these initiatives seek to improve access to and the re-use of industrial data, broadening the scope of open data. This positions Europe as a leader in the data-driven economy.
Open Data Benefits for Businesses
Open data can help bring diverse benefits to governments, businesses, customers and civil society. This is outlined in the European Data Portal 2020 study, The Economic Impact of Open Data: Opportunities for value creation in Europe. The report highlights efficiency gains and cost savings of open data across sectors.
It showed that 49% of the data used by surveyed organisations is open data and 77% of organisations plan to use more data. Meanwhile, 46% of organisations’ revenues are impacted by open data, and 73% of organisations expect the impact to increase.
Among the top benefits of open data opportunity outlined in the report were improved efficiency and cost savings in public sector. Yet that’s not everything - open data is also seen as a driver for economic growth. It can contribute to the development of innovative services and new business models.
Moreover, it can help organisations make more informed decisions and better use of existing resources. Companies re-use open data to gather meaningful insights, develop applications, or enhance existing products or services. Some of the benefits of open data for businesses include:
- Improved Revenues & Profits: Open data can increase business income and the overall value produced by a service or product.
- Cost Savings: Open data can reduce the number of jobs needed to offer a service, saving on labour.
- Innovation: Open data can encourage innovation by providing the foundation for creating new products and services.
- Better Customer Experience: Applications utilising open data can save users time by streamlining tasks.
- Knowledge Economy: Open data contributes to the expansion of the knowledge economy, enhancing information-based services and products.
Open Data Use Cases Across Sectors
Let’s take a look at how open data can benefit various types of companies.
E-Commerce
Open banking payments are already enhancing e-commerce by improving the shopping experience and reducing costs for sellers. Open data can further help online retailers in analysing the market. It can offer insights into consumers' likes and wants, helping create more focused marketing efforts.
Travel
Open banking already helps travel merchants by making cross-border payments easier. The open data economy can further assist by providing live updates on transport times and delays, which can help manage travel firms' operations.
SaaS
For software-as-a-service (SaaS) businesses, open data can enhance features and functionalities within their products. It can improve customer insights with data enrichment tools, and enable more sophisticated open data analytics services.
Education Platforms
Education platforms can leverage open data to curate personalised learning experiences. For example, education companies with open data would be able to integrate real-time information into curriculums. Again, they could gain better user insights with data enrichment.
Future of Open Data: Trends & Forecasts
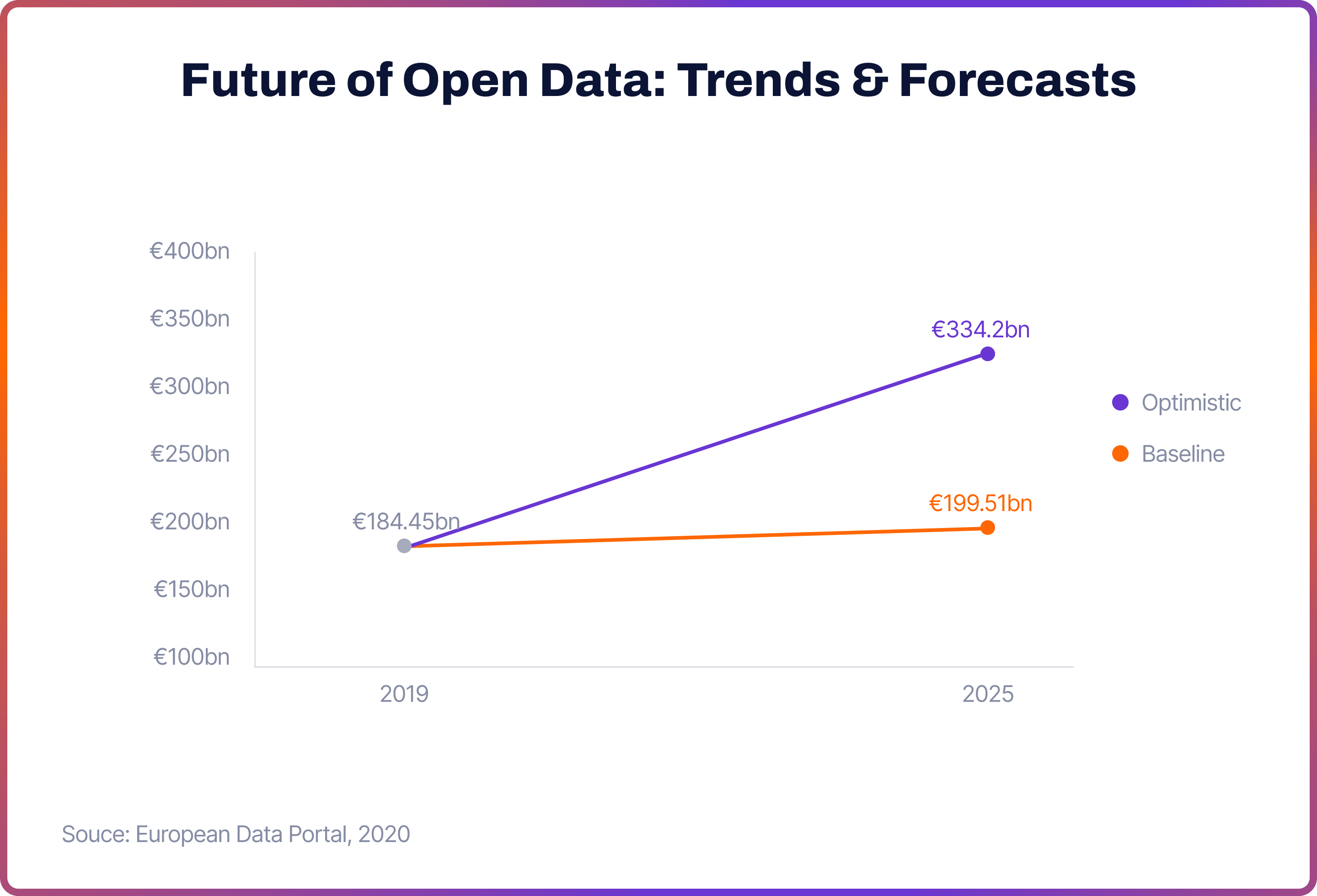
The European Data Portal 2020 study estimated that the open data market size was €184bn in 2020, and forecast it to reach between €199.51bn and €334.21bn in 2025. The report also forecasts that open data employment will increase to between 1.122 million to 1.972 million jobs in the EU by 2025.
Regulations play a crucial role in promoting the use of open data worldwide, driving its expansion and adoption. As this trend continues, we'll see even more industries and sectors leveraging open data to innovate and improve their services. This progress marks a promising future for the open data economy, with broad implications for businesses, employment, and societal benefits.
Open Banking with Noda
Elevate your business with Noda’s payments and open banking solution. Our all-in-one platform uses cutting-edge AI and machine-learning technologies.
Noda is a worldwide payment and open banking provider for instant business transactions. We operate in the EU and Canada, supporting a wide range of currencies for globally-minded clients. Noda offers partnerships for businesses of all types and sizes, with scalable plans to fuel your growth and meet your needs.
FAQs
What is open data in simple terms?
Open data is information that's freely available for anyone to use, share, and modify. Open data in governments is a widely accepted standard, yet it can also apply to other organisations and businesses.
What is the value of open data in business?
In business, open data's value lies in fostering innovation, enabling smarter decision-making through access to insights and trends, and enhancing transparency and engagement with stakeholders.
What is the difference between open data and closed data?
Open data differs from closed data in its accessibility; open data is available to all without restrictions, while closed data is controlled and can only be accessed by certain people or groups, often for privacy or security reasons.
Latest from Noda

Top Payment Methods in Austria: How to Accept Payments Efficiently in 2026

GoCardless Review 2026: What Merchants Need to Know

AIS vs PIS in Open Banking: What’s the Difference & When to Use Each