In today's digital era, businesses recognise the importance of seamless transactions. To achieve this, payment gateways play a crucial role.
Acting as the middleman, they enable secure and efficient transactions, ultimately boosting customer satisfaction and overall business growth. Not only do payment gateways streamline the payment process, but they also ensure that sensitive financial data remains secure, fostering trust between businesses and customers.
Here, we take a look at the different types of online payment gateways and how to choose the best option for your business.
What is a Payment Gateway?
A payment gateway is an important technology in the payments world, which allows businesses to accept and process debit or credit card transactions, whether they are conducted online or in-person. It serves as a middleman, securely transmitting transaction details between the customer, merchant, payment processor and financial institutions. In payment processing, a payment gateway comes in between the customer checkout and the payment processor.
Types of Payment Gateways in E-commerce
Payment gateway systems come in various types, each with its unique features tailored to different business needs. Let’s take a look at the key types of payment gateway integration.
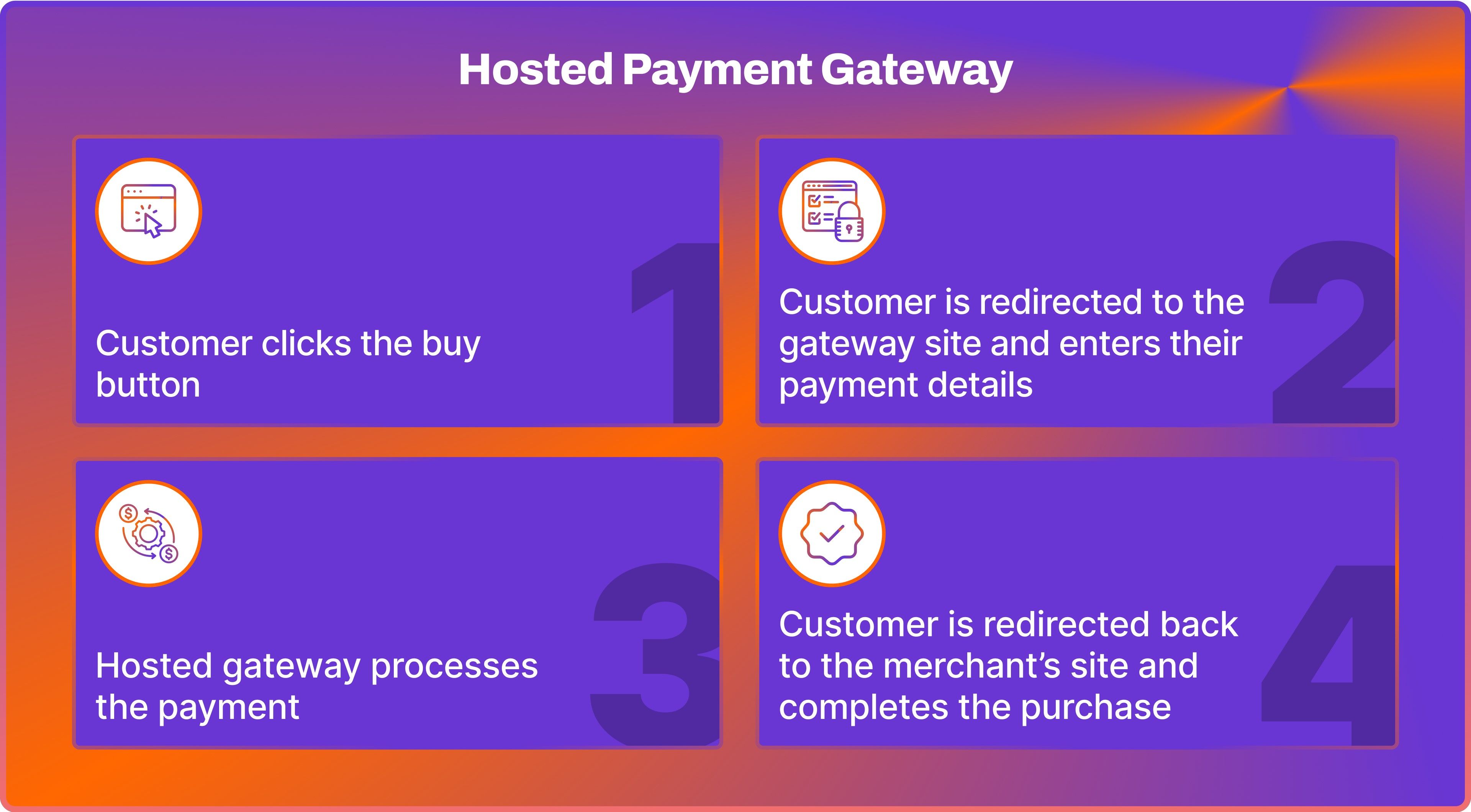
Hosted Payment Gateway
Hosted payment gateways, also known as the redirect method or third-party payment gateway, provide customers with a seamless payment experience. When customers choose to make a payment, they are redirected to the secure platform of the payment processor where they can enter their payment details. Once the payment is processed, they are then redirected back to the merchant's website.
This payment gateway type is popular among businesses that prioritise convenience and security as it allows them to avoid directly handling sensitive payment data. Integration is simple and comes with built-in security measures.
Pros
- Simplified integration: Requires minimal technical expertise.
- Enhanced security: The payment processing is handled by the gateway provider, ensuring PCI DSS compliance.
Cons
- Interrupted user experience: The redirection can be a tad jarring for some customers.
- Less customisation: Merchants have limited control over the payment page's look and feel.
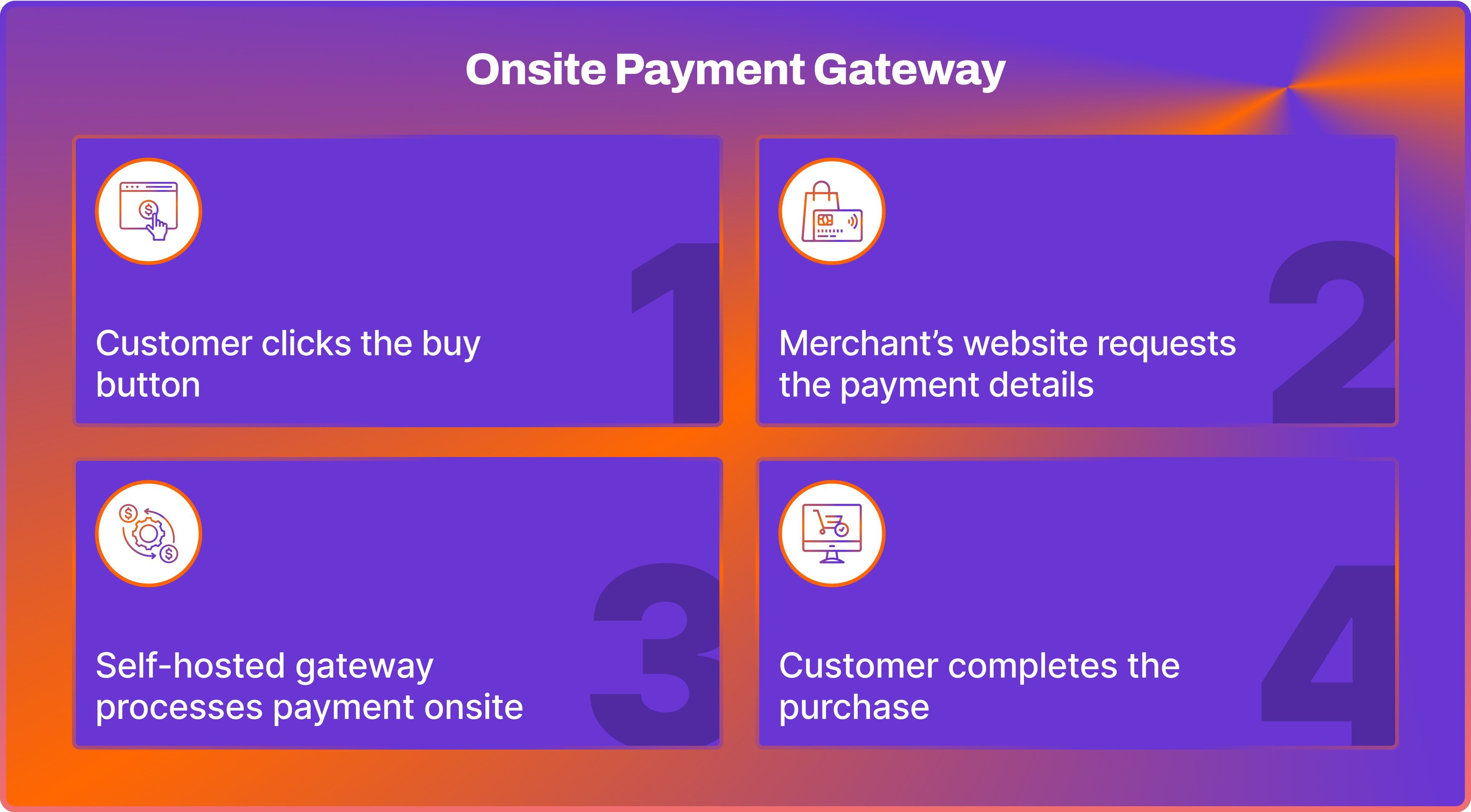
Onsite (Self-hosted) Payment Gateway
With onsite or self-hosted payment gateway infrastructure, merchants can collect payment information directly on their website. The payment data is securely transmitted from the merchant's server to the payment gateway's server for processing.
This payment gateway option, often known as a direct gateway, offers a seamless and uninterrupted user experience since customers are not redirected elsewhere.
Pros
- Seamless user experience: Customers enjoy a smooth transaction without redirection.
- Customisable: Merchants have more control over the payment page's design, aligning it with their brand aesthetics.
Cons
- Increased security responsibility: Merchants need to ensure robust security measures to protect sensitive payment data.
- Technical expertise required: The integration demands a higher level of technical knowledge.
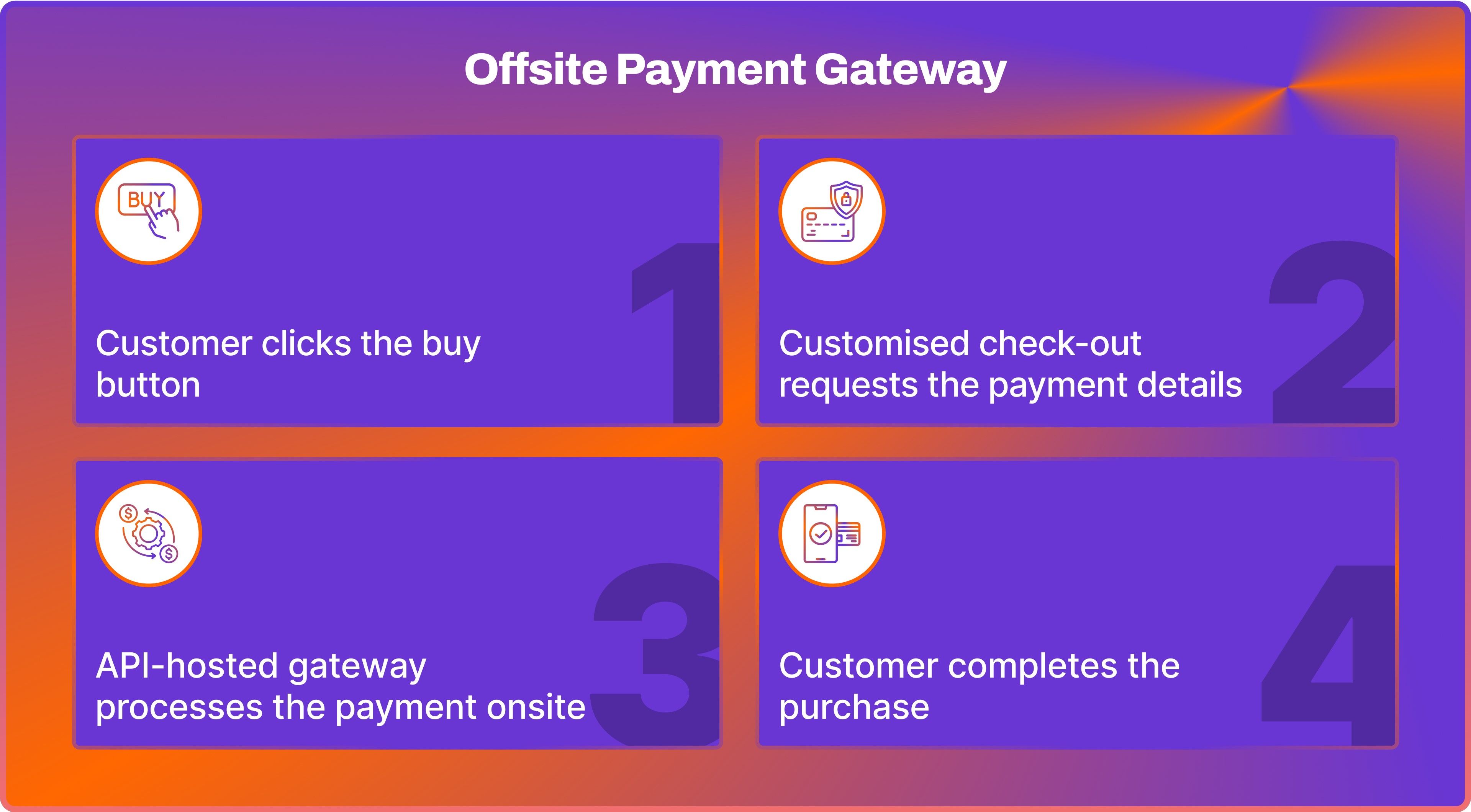
Offsite (API-hosted) Payment Gateway
By utilising an Application Programming Interface (API), these gateways enable merchants to transmit payment information directly to the payment processor without any sensitive data being stored on their own servers.
While customer payment data is collected on the merchant's site, the actual processing occurs offsite, guaranteeing a secure transaction environment.
Pros
- Seamless user experience: Customers stay on the merchant's site during the transaction, providing a smooth checkout experience.
- Enhanced security: Since no sensitive data is stored on the merchant's server, the risk of data breaches is significantly reduced.
Cons
- Technical expertise required: Integration requires a higher level of technical knowledge.
- Compliance responsibility: Merchants need to ensure their systems comply with the necessary security standards.
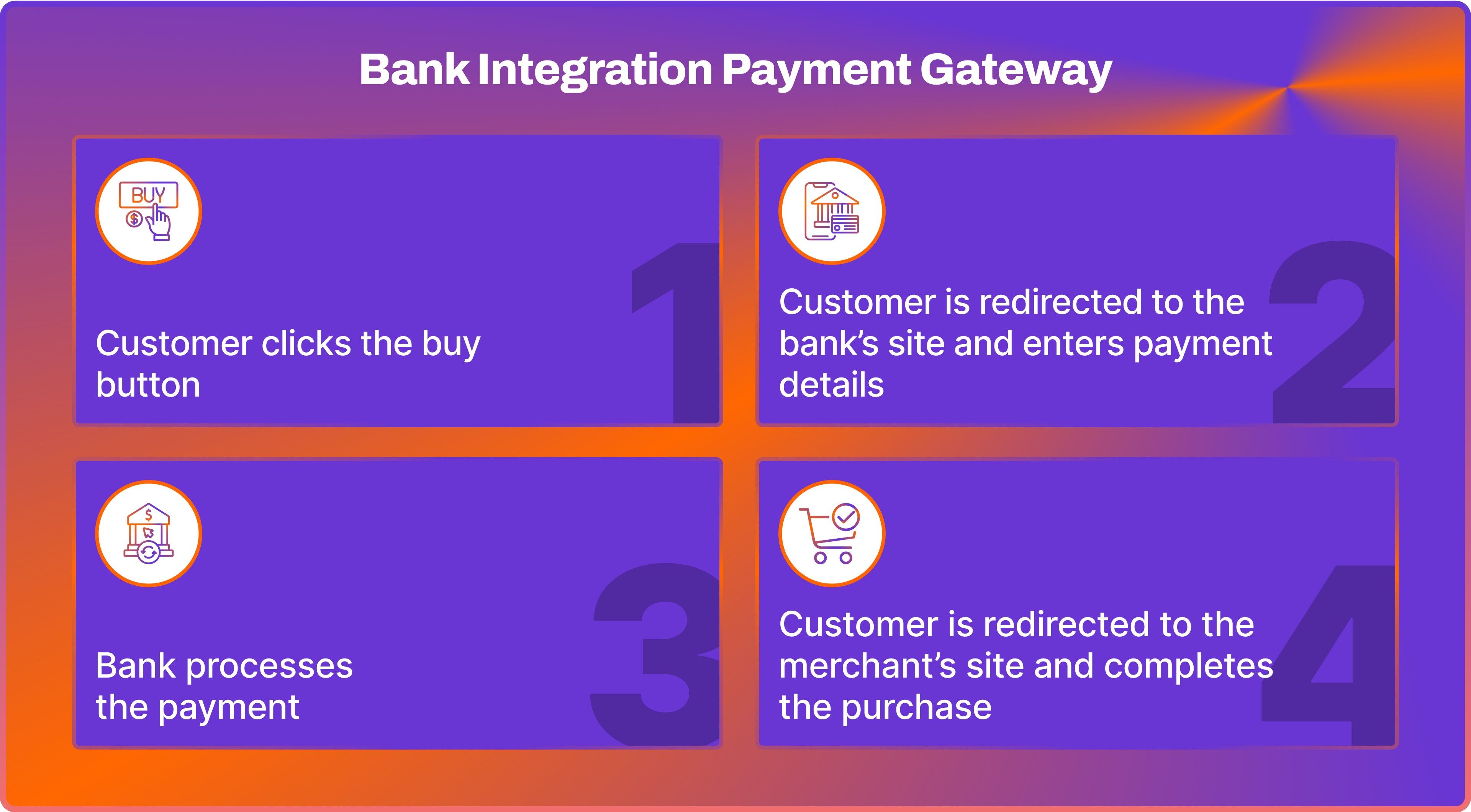
Local Bank Integration Payment Gateway
The local bank integration process involves establishing a direct connection between a merchant and a local bank. When a customer makes a payment, the transaction details are sent directly to the local bank for processing.
Once approved, the funds are then transferred from the customer's bank account to the merchant's bank account. This example of a payment gateway is favoured for its straightforward and convenient nature.
Pros
- Simplified transactions: Direct bank connections simplify the transaction process, making it straightforward for both merchants and customers.
- Lower fees: Typically, local bank integration incurs lower transaction fees compared to other payment gateway solutions.
Cons
- Limited to local transactions: This method is usually restricted to local transactions, limiting international sales.
- Bank approval required: Merchants need to obtain approval from banks, which can be a lengthy and sometimes challenging process.
How to Choose the Payment Gateway Type for Your Business
Choosing the right payment gateway is essential for ensuring seamless and secure transactions in your business. Several factors come into play when making this decision, including your business model, technical capabilities, and customer preferences.
Firstly, determine whether your business operates primarily online, offline, or in a hybrid model, as different gateway types are suited to different business models.
Secondly, consider the technical expertise available within your team since certain gateway types may require more technical knowledge for integration than others.
When considering gateway options, it's important to take into account the user experience provided by each type. Onsite gateways offer a seamless experience but require strong security measures.
Security should be a top priority, so make sure the chosen gateway type adheres to industry standards like PCI DSS and offers features such as tokenisation and 3D Secure authentication.
Another crucial aspect is understanding the costs involved, including transaction fees, monthly charges, and any other associated expenses related to the chosen gateway type.
When choosing a payment gateway for your e-commerce platform or website, it's important to consider how easily it can integrate with your existing system. Some gateway types may offer smoother integration than others. Additionally, make sure the chosen gateway supports a wide range of payment methods and currencies, especially if you have customers from around the world.
Another crucial factor is the level of customer support provided by the company offering the gateway services. It's essential to have prompt and reliable assistance in resolving any issues that may arise. Consider the customisation options available with the chosen gateway type as well. You'll want it to align with your brand aesthetics seamlessly.
Finally, assess the performance metrics, uptime guarantees, and overall reliability of the selected gateway type. These factors will ensure smooth and secure transactions for your customers.
Merchants can effectively select a payment gateway by carefully evaluating these factors. This will ensure that the chosen gateway aligns with their specific business requirements, resulting in a secure and seamless transaction experience for customers. Ultimately, this fosters business growth.
FAQs
How many types of payment gateways are there?
There are four most popular payment gateway types. These include hosted, self-hosted, API-hosted and local bank integration.
What are the types of payment gateway?
The main types of payment gateways include hosted, self-hosted, API-hosted and local bank integration.
What is a self-hosted payment gateway?
With a self-hosted payment gateway, merchants can collect payment information directly on their website. This means that customers don't need to be redirected away, providing a seamless and uninterrupted user experience. The payment data is securely transmitted from the merchant's server to the payment gateway's server for processing, ensuring the safety of sensitive information.
What is an API-hosted payment gateway?
An API-hosted payment gateway, also known as an offsite payment gateway, acts as a connection between a merchant's website and a payment processing network via an API (Application Programming Interface). This setup allows the merchant to collect the customer's payment information on their site while securely processing the transaction offsite. By handling the processing externally, this approach ensures a secure environment for transactions without storing any sensitive data on the merchant's servers.
What is a hosted payment gateway?
A hosted payment gateway is a convenient solution for businesses that want to avoid handling payment data directly. When customers choose to make a payment, they are redirected to the payment gateway's platform. There, they enter their payment details, and once the transaction is complete, they are redirected back to the merchant's website. This method offers the simplicity of integration and includes built-in security measures.
Latest from Noda
Digital Payment Trends: Navigating the Future

Payment Methods in Ireland in 2026: Everything You Need to Know

Top Payment Methods in Austria: How to Accept Payments Efficiently in 2026