A financial revolution is currently underway – and its name is open banking. The new concept is breaking down the walls of the traditional financial industry, creating endless possibilities and prospects for merchants and customers.
Open banking utilises cutting-edge technology and encourages collaboration, transforming how we manage our finances, access services, and foster innovation.
Now, let’s have open banking explained in detail, exploring the technology behind it and its benefits, use cases, and the exciting prospects it offers for the industry's future.
What is open banking?
Open banking is a new efficient way to manage finances, make direct payments, and avoid extra costs. It allows merchants to securely access customer banking information with their consent. This helps understand their spending habits, preferences, and creditworthiness. With this knowledge, merchants can offer products and services that better suit their customers.
Open banking also makes it easy to try new payment options. It connects banks, payment providers, and fintech companies to provide streamlined and convenient payment experiences. This includes direct bank transfers, instant payments, and even personalised financing features, creating flexibility for customers and reducing friction in the purchasing process.
Open banking relies on application programming interfaces (APIs) to make all this possible. They act as the bridge facilitating secure and seamless financial data sharing between banks, merchants, and other financial service providers.
Open banking API technology
APIs allow merchants to connect their systems directly with the systems of banks and other financial institutions, enabling the exchange of information in a standardised and efficient manner.
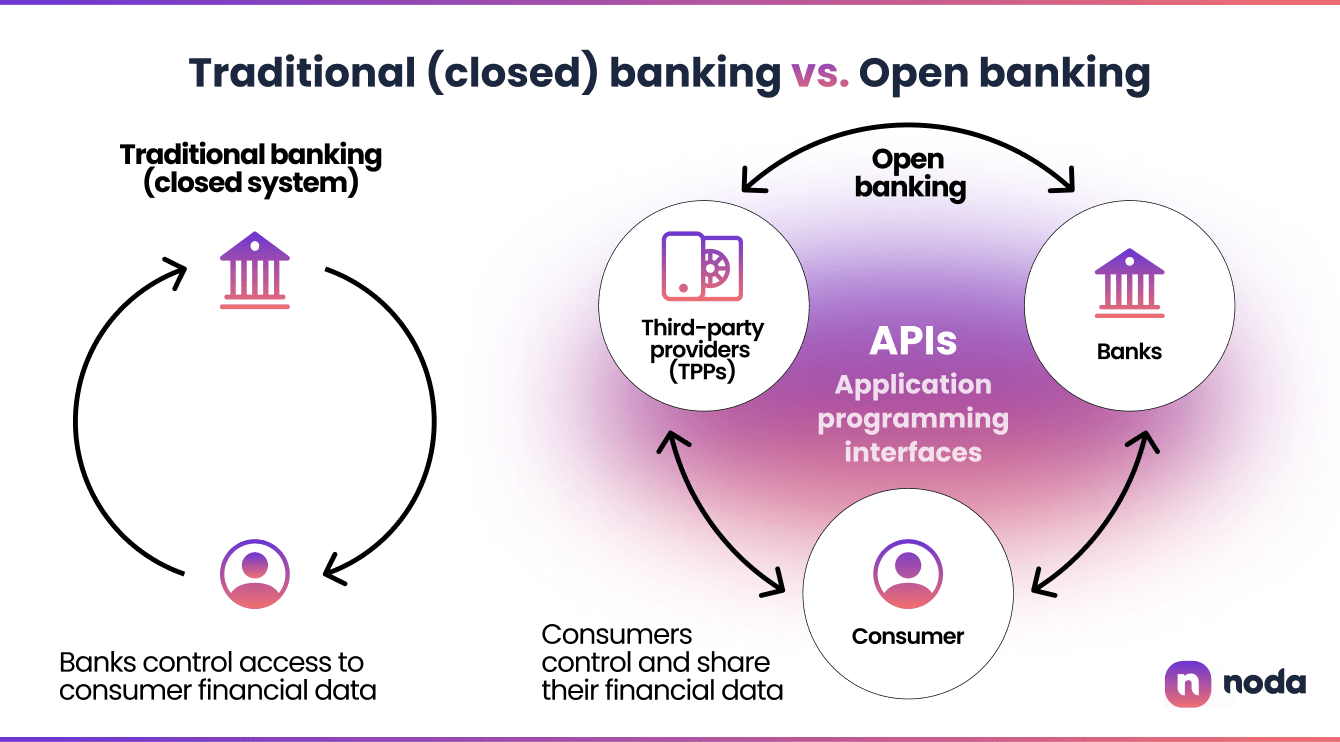
How does open banking work?
Open banking allows individuals and businesses to share their financial information securely and efficiently with authorised third-party providers (TPPs) through APIs. It enables customers to consent to access their banking data by other organisations, such as fintech companies or banks.
Here's a general overview of how open banking works:
Customer consent: Open banking relies on customer consent. When customers choose to participate, they grant permission for their banking data to be shared securely with authorised third-party providers, including merchants. This consent ensures data privacy and protects customer information.
API connectivity: APIs enable the secure exchange of data between different systems. Merchants can integrate their systems with banks and financial institutions through APIs, allowing them to access customer banking data and initiate transactions.
Data access: Once connected through APIs, merchants can access relevant customer financial data, such as account balances, transaction history, and spending patterns. This real-time access to data provides valuable insights into customer behaviour and preferences, allowing merchants to make informed business decisions.
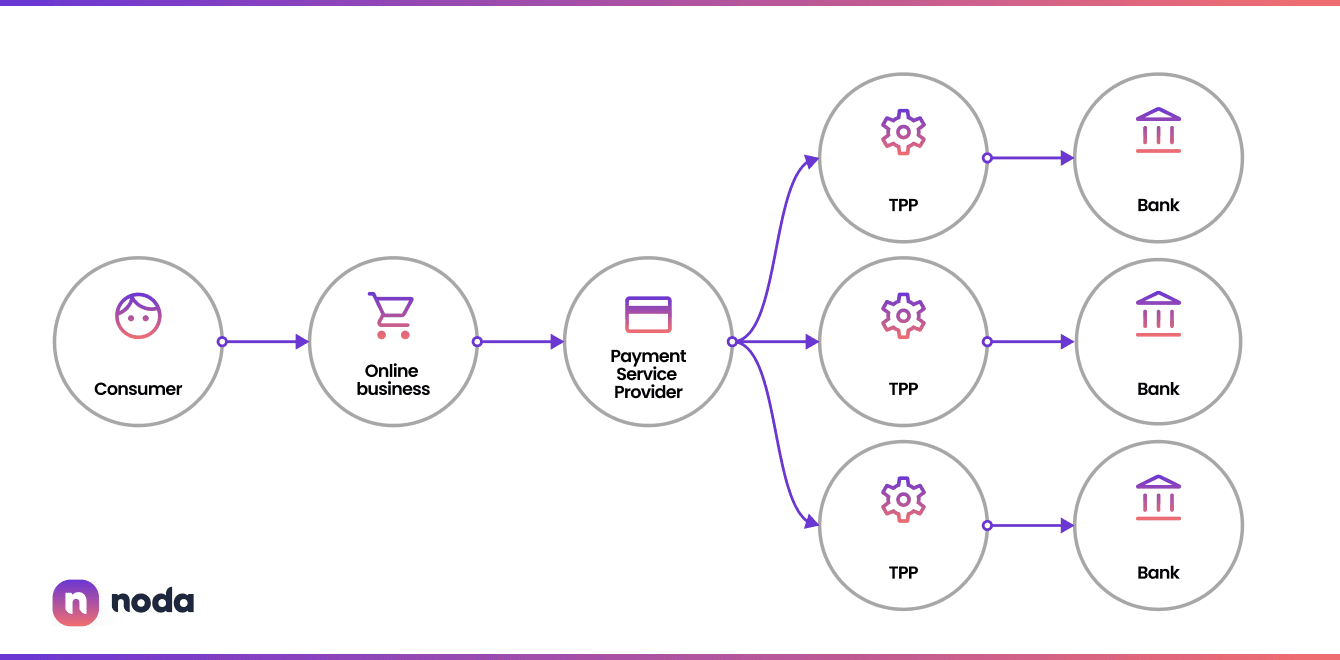
Payment options: Open banking offers merchants various payment options beyond traditional methods. They can integrate with payment service providers and financial institutions through APIs to provide seamless and convenient payment experiences. This includes options like direct bank transfers, instant payments, and mobile wallets, giving customers more flexibility and choice during checkout.
Streamlined operations: APIs in open banking automate processes and streamline operations for merchants. For example, merchants can automate reconciliation processes by accessing real-time transaction data, eliminating manual efforts and reducing errors. This leads to more efficient financial management and improved cash flow.
It's important to note that the specifics of open banking can vary depending on the regulatory framework in a particular country or region. Different jurisdictions have their own guidelines and requirements for implementation, aiming to balance promoting competition and innovation while safeguarding customer data and privacy.
The role of PSD2 in open banking
PSD2 (Second Payment Services Directive) is an essential aspect of open banking, a payments legislation introduced by the European Union in September 2019. It gives EU consumers the right to "data portability" and greater flexibility in their financial information. PSD2 has put Europe at the very centre of open banking due to the new legal and technological landscape it has enabled.
The importance of PSD2 rests on the European regulatory framework that permits third parties to receive verified and safe access to accounts to manage payment details. Open banking payments can now be triggered with the approval of customers.
Due to PSD2, all banks must now deal with payments initiated by legitimate third-party service providers known as PISPs (Payment Initiation Service Providers). Open banking has become a convenient new way for consumers to use online bank payments to fund merchants.
The security underpinning PSD2
At the heart of PSD2 is the requirement for merchants to uphold Strong Customer Authentication (SCA). To ensure security and fraud prevention, merchants must add tools to their online checkout or payment point that meet authentication requirements (introduced in the EEA by January 2021 and in the UK by March 2022).
Merchants must adopt a range of security measures specified, such as passwords, PINs, tokens, fingerprints, or other accepted forms of security identification.
PISPs, fintech developers, and merchants are now hard at work meeting the challenges of these security measures.
Why is open banking important?
Over the past 15 years, there has been a significant transformation in the shopping, banking, and payment processing sectors, marked by the decline of cash payments and the rise of card transactions and online shopping. The recent Covid-19 pandemic has further accelerated this shift, as digital channels have fully emerged, leading to a surge in e-customers and mobile eCommerce.
This evolution has profoundly impacted the online banking sector, with more than 75% of banking clients in North America and Europe now conducting most of their transactions online.
Moreover, the rising popularity of tap-to-pay transactions, QR codes, and other payment innovations has contributed to the changing landscape of payment channels. As a result, the global online banking market is experiencing rapid transformation and is expected to be worth $11 trillion by 2030.
Open banking examples of use cases
Below are a few examples of how open banking is being implemented and the types of services it enables.
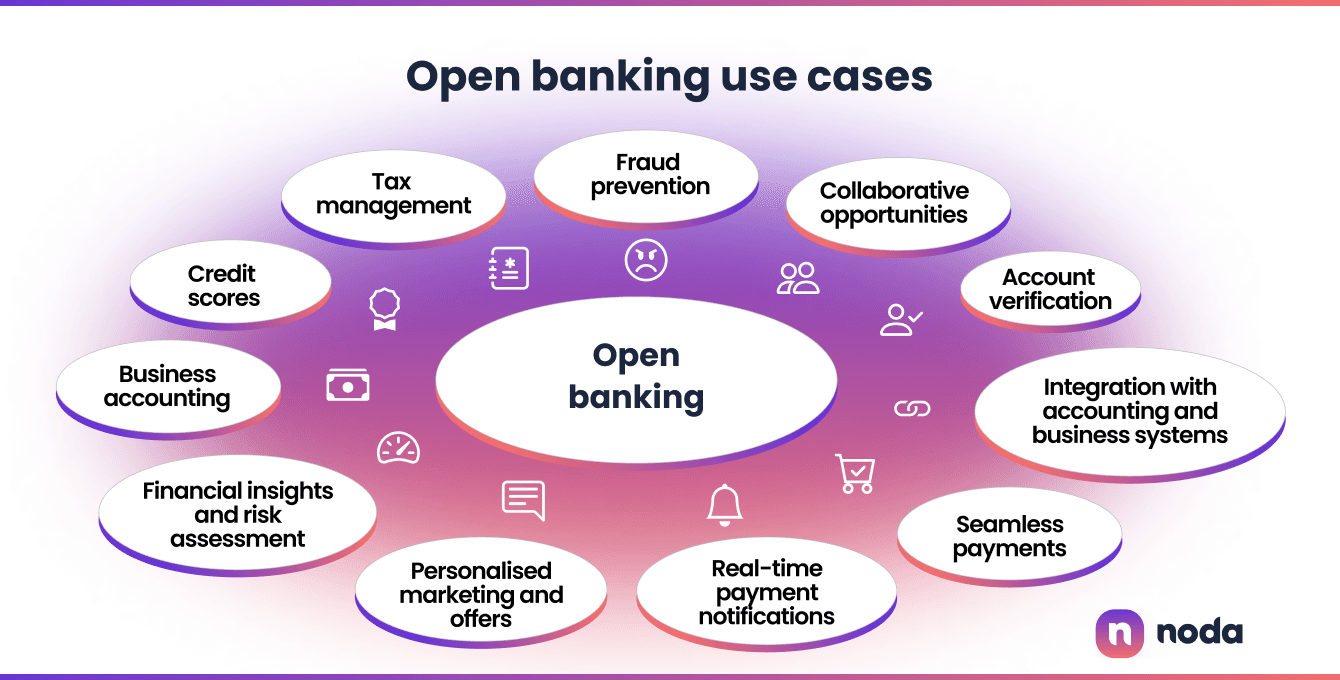
Account verification
Open banking allows merchants to verify customers' bank account information instantly. This streamlines the onboarding process by removing the need for manual document submission or traditional credit checks.
Merchants can authenticate the account details provided by customers, reducing the risk of fraud and ensuring accurate payments.
Integration with accounting and business systems
Open banking APIs facilitate financial data integration directly into merchants' accounting and business systems. This automation streamlines financial management processes, such as reconciliations, cash flow monitoring, and reporting.
Merchants can save time, reduce manual errors, and gain accurate insights into their financial performance.
Seamless payments
Open banking APIs enable merchants to offer convenient and seamless payment options to their customers. Customers can initiate payments directly from their bank accounts, bypassing the need for third-party payment processors.
This leads to faster and more secure transactions, reducing payment processing costs for merchants.
Real-time payment notifications
Open banking allows merchants to receive real-time payment notifications when a customer initiates a transaction. This instantly confirms successful payments and enables faster order fulfilment or service delivery.
Merchants can enhance customer satisfaction by providing timely updates and improving the shopping experience.
Personalised marketing and offers
With access to customer financial data, merchants can gain valuable insights into their customers' spending habits, transaction history, and preferences. This information enables merchants to create personalised marketing campaigns and tailored offers that resonate with individual customers.
Merchants can enhance customer engagement, increase conversion rates, and foster loyalty by delivering targeted promotions.
Financial insights and risk assessment
By accessing customer financial data, merchants can gain a deeper understanding of their customer's financial health. This information can be used for risk assessment and credit scoring, enabling merchants to make informed decisions regarding credit extensions or instalment plans.
Merchants can tailor their offerings based on customers' financial capabilities, reducing the risk of defaults and improving overall credit management.
Business accounting
Open banking APIs offer small businesses a streamlined accounting process by automating the collection and categorisation of financial data, encompassing revenue and expenses.
This automation eliminates manual data entry, saving businesses valuable time and reducing costs.
Credit scores
Open banking gives a more in-depth and personalised look at a consumer's credit history by combining data from multiple sources.
This helps to provide a more accurate picture of an individual's creditworthiness and financial history.
Tax management
Open banking APIs offer valuable assistance in tax management for businesses and individual taxpayers by providing real-time visibility into financial data. They help users stay informed about their tax obligations, making the process more convenient. Moreover, APIs facilitate direct filing with tax agencies, streamlining the tax filing process.
Moreover, open banking apps equipped with self-employed and small business accounting features allow users to track expenses and income, ensuring accurate and organised financial records for tax purposes.
Fraud prevention
Open banking enables real-time monitoring of transactions, helping detect suspicious activities and potential fraud. Banks and financial institutions can enhance their fraud detection capabilities by analysing data from multiple sources.
Collaborative opportunities
Open banking encourages collaboration between merchants and financial service providers. Merchants can partner with banks, fintech companies, or other third-party providers to offer value-added services.
This may include access to financing options, insurance products, or loyalty programs, enhancing the overall customer experience and expanding revenue streams for merchants.
Benefits of open banking
Advantages for merchants
The rapid development of open banking trends presents an excellent opportunity for merchants, empowering consumers and businesses. Online banking payments' seamless, secure, and user-friendly nature enables instant fund transfers from customer bank accounts directly to merchants.
As a result, merchants can enjoy a range of benefits:
- Increased conversion rate
Offering a seamless and comfortable customer journey, particularly during the checkout or point of payment, provides a significant advantage for merchants. With more efficient payment processing through open banking, customers experience reduced hassle, heightened satisfaction, and increased loyalty towards brands and services.
As payment by bank transfer continues to grow and potentially becomes the leading payment method, merchants who seize the opportunity at the right time are poised to maximise conversions and drive business growth.
- Lower fees
One of the most prominent benefits of open banking payments is the ability for merchants to lower their processing costs and gain fee flexibility by selecting the appropriate service. Merchants can bypass traditional intermediaries, such as card networks, that have historically held significant control.
- Fraud prevention
Open banking leverages existing bank structures, providing an inherent advantage of bank-level security, robust encryption (256-bit), and multi-factor authentication. Customers can use their bank login details for payments, eliminating the need to share additional information.
The established security measures ensure fraud prevention and often result in minimal or zero chargebacks, further enhancing the reliability and safety of open banking transactions.
- Greater transparency
The near-instantaneous processing of payments brings satisfaction to both merchants and consumers. Witnessing a payment being processed almost immediately fosters trust and confidence in the transaction.
Additionally, the speed of instant payments significantly contributes to improved cash flow for merchants, enabling quicker access to funds and facilitating more efficient financial management.
- Instant refunds
With the integration of appropriate technology, such as PISPs, open banking enables merchants to provide instant refunds to customers. This efficient process ensures that refunds are delivered immediately, reinforcing customer satisfaction and building stronger brand loyalty.
- Cross-border flexibility
By utilising open banking with a comprehensive PISP, merchants gain geographical efficiency in managing payments across various currencies and payment types. They can seamlessly handle currency payment processing, including conversions in cross-border transactions.
Open banking's capabilities enable merchants to expand their reach and cater to customers worldwide.
Advantages for customers
The reason behind the popularity of online bank payments is quite simple – consumers get satisfaction and security from making direct payments from their bank accounts.
The benefits of online bank payments are clear and easy to understand:
- Ease of use
Open banking payments are highly efficient due to the streamlined process that requires customers to confirm their payment service only once. Once validated, customers can conveniently make direct payments from their bank accounts at any time without using cards or providing additional details.
- Security
Open banking instils a strong sense of trust among consumers, as it relies on their personal bank accounts, which have inherent security guarantees. This trust extends to all open banking activities, ensuring that every purchase, whether online subscription or payment for goods, is conducted securely and reliably.
- Speed
Open banking has dramatically benefited from the advent of instant transfers, which have become possible only recently. The availability of real-time fund transfers has brought about a significant positive impact on open banking by enhancing both confidence and convenience in payment processes.
With the ability to send funds instantly, consumers can enjoy faster access to subscriptions, tickets, and other services.
Is open banking safe?
Open banking, as a concept, has the potential to revolutionise the financial industry by promoting innovation, competition, and customer empowerment. It aims to give individuals greater control over their financial data and enable them to securely share it with authorised third-party providers, fostering the development of innovative financial products and services.
While open banking holds significant promise, concerns around safety and security naturally arise.
It is essential to recognise that open banking is designed with security and privacy in mind. Robust security measures and protocols are put in place to protect the sensitive financial information of individuals. These measures typically involve strong encryption, secure APIs and stringent authentication processes. Financial institutions and third-party providers must adhere to strict regulatory standards to ensure data protection, including compliance with the European Union's frameworks, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
However, like any technological innovation, open banking is not without risks.
Cybercriminals constantly evolve tactics to exploit vulnerabilities, and unauthorised access to financial data can result in various fraudulent activities. To mitigate these risks, industry stakeholders, including regulators, financial institutions, and technology providers, work together to establish comprehensive security frameworks and standards. Continuous monitoring, threat detection, and robust authentication mechanisms safeguard against unauthorised access, data breaches, and fraudulent activities.
Customers, too, play a crucial role in ensuring the safety of their financial information in an open banking environment. It is essential to exercise caution and carefully choose trustworthy third-party providers, preferably those authorised and regulated by relevant authorities. Being vigilant about the permissions granted and regularly reviewing account activities can help identify suspicious transactions or potential breaches.
FAQs
How will open banking affect banks?
Open banking has the potential to impact banks in a variety of ways, including:
- Partnership opportunities. Collaboration between banks and fintech companies will enhance product offerings and expand market reach.
- New revenue streams. Open banking will bring new revenue streams and possibilities for banks, including personalised products and data monetisation.
- Business model transformation. Banks will have to adopt open APIs, update systems, and embrace agile technologies to adapt to an open banking environment.
In the meantime, banks will also have to adjust to the changing environment within the following fields:
- Increased competition. As open banking allows third-party providers (TPPs) to access customer data, traditional banks will face increased competition from fintech companies offering innovative products and services.
- Customer-centric approach. Banks will have to prioritise customer satisfaction and provide personalised services to keep retention in an open banking ecosystem.
- Data sharing and security. Banks will have to invest in newer security measures to address privacy concerns and protect customer data.
Which banks use open banking?
Open banking has gained traction globally, and many banks have embraced its principles to varying degrees. A few notable examples of banks that have implemented open banking initiatives are:
- HSBC, one of the world's largest banking and financial services organisations
- ING, a Dutch multinational banking and financial services corporation
- Santander, a global banking group
- Barclays, a major UK-based bank
- BBVA, a Spanish multinational bank
Open banking adoption and implementation may vary among banks, and the examples provided above only represent a small fraction of a rather extensive list. Additionally, the availability and extent of open banking services may differ based on the specific country and regulatory environment in which the banks operate.
What does open banking allow?
By definition, open banking brings a revolutionary change to how financial information is shared and accessed. With the help of APIs, it allows customers to securely grant access to their financial data.
- Account Information Services (AIS) allow customers to view and aggregate data from multiple institutions, gaining a holistic understanding of their finances;
- Payment Initiation Services (PIS) allow customers to make direct payments from bank accounts, enhancing convenience and speed.
Open banking fosters innovation and competition, leading to personalised financial products and services.
What is open banking architecture?
Open banking architecture is the technical framework and structure enabling open banking solutions. It includes the design principles, protocols, and components necessary for secure data sharing and seamless integration of financial services.
The architecture incorporates APIs for communication, consent management for customer data control, robust security measures, and standardised data formats and structures.
With a well-designed architecture, open banking platforms can securely and efficiently facilitate the sharing of financial data, promote innovation, and enhance the overall banking experience for customers.
Latest from Noda

Payment Methods in Ireland in 2026: Everything You Need to Know

Top Payment Methods in Austria: How to Accept Payments Efficiently in 2026

GoCardless Review 2026: What Merchants Need to Know
