Biometrics refers to the measurement and statistical analysis of individuals' unique physical and behavioural traits. This technology primarily serves the purposes of identification, access control, and surveillance. Biometrics offer a layer of security intrinsically linked to an individual, making it a powerful tool in preventing data breaches and unauthorised access.
Types of Biometrics Explained
Biometrics can be categorised into three main groups:
- Biological Biometrics: These include traits at a genetic and molecular level, such as DNA or blood.
- Morphological Biometrics: These involve the structure of your body, such as your eye, fingerprint, or the shape of your face.
- Behavioral Biometrics: These are based on patterns unique to each person, such as how you walk, speak, or type on a keyboard.
How Biometrics Security Works
Biometric security operates by acquiring and mapping unique biometric data. This data is then stored and compared with future access attempts. It is commonly encrypted and stored either within the device itself or on a remote server.
Biometric scanners, as hardware devices, capture biometrics for identity verification. These scans are compared against the stored database to grant or deny system access. An individual's body features serve as the "key" to unlock their entry.
Basic Mechanisms
Biometric systems typically include three components.
- First, a reader or scanning device captures the biometric factor being authenticated.
- Then, specialised software converts the scanned biometric data into a standardised digital format and compares match points with stored data.
- Lastly, a secure database is utilised to store and retrieve the biometric data for comparison purposes.
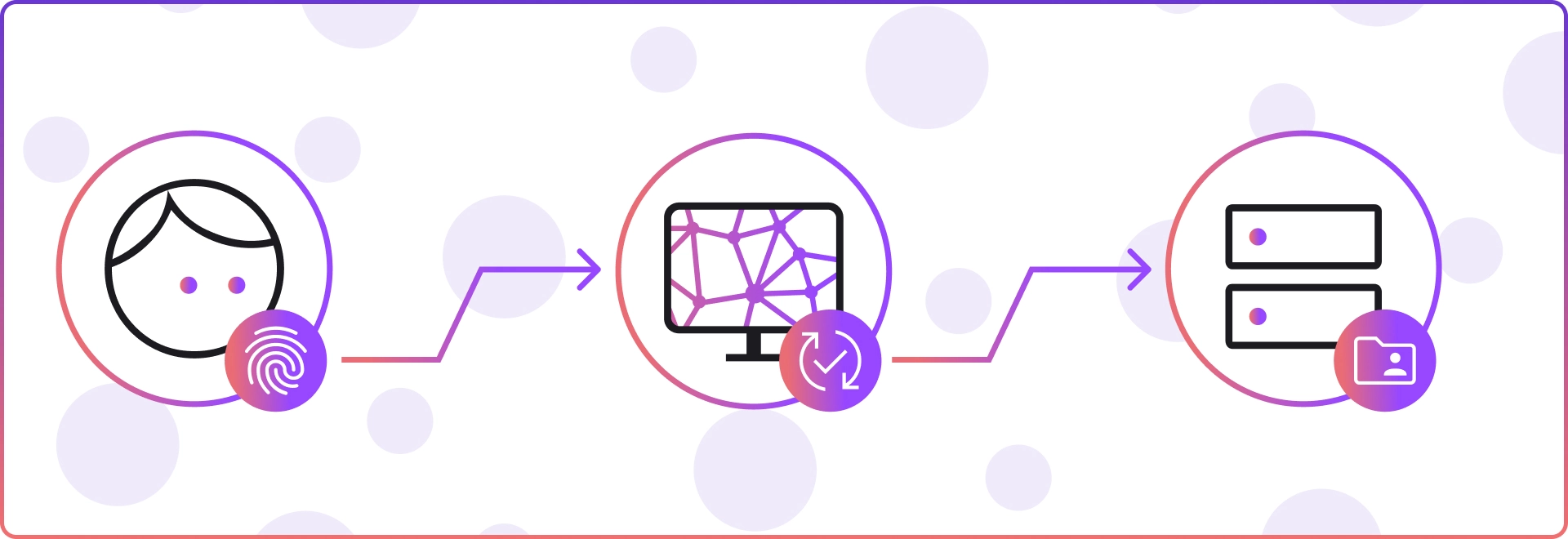
Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication involves comparing a person's data for specific characteristics with their biometric "template" to determine similarity. The reference model is initially stored in a database or a secure portable element, like a smart card. Subsequently, the stored data is compared to the individual's biometric data to confirm their identity.
Biometric Identification
Biometric identification involves determining a person's identity by capturing their biometric data. This can include photographs of their face, voice recordings, or fingerprint images. The collected data is then compared to the biometric information stored in a database for multiple individuals.
Biometrics Security and Financial Data
Biometrics are transforming financial data security by providing unique and difficult-to-counterfeit authentication.
Financial institutions, fintech and banks are progressively integrating biometric technologies, including facial recognition, ECG-reading bracelets, and voice recognition, into their security protocols. These measures enhance both user experience and security by replacing or improving traditional methods like passwords and PINs.
Biometrics also find application in corporate environments to regulate access to sensitive financial data and prevent fraudulent activities.
Nevertheless, while offering robust security, biometrics should be part of a multi-layered strategy. With advancing technology, the role and meaning of biometrics in ensuring financial data security is expected to grow significantly.
Benefits of Biometric Security
- Hard to Fake or Steal: Unlike passwords, biometric data is unique to each individual and cannot be easily replicated or stolen.
- Convenience: Biometrics are always with you and cannot be lost or forgotten.
- Efficiency: Biometric templates take up less storage.
- Nontransferable: Biometric data is intrinsically linked to the individual and cannot be transferred.
Examples of Biometrics in Use
- Voice Recognition: Used in customer service and smart home devices.
- Fingerprint Scanning: Commonly used in smartphones and laptops.
- Facial Recognition: Used in smartphone unlock systems and surveillance.
- Iris Recognition: Used in high-security areas.
- Heart-Rate Sensors: Used in health and fitness tracking.