The momentum of open banking in Germany post-PSD2 is growing since 2020, as the adoption of open banking has been steadily growing in the region. Germany, renowned for its innovative prowess, is one of the most mature open banking infrastructures in Europe.
As the financial landscape evolves, it is vital for business leaders and executives to grasp the intricacies and opportunities brought forth by open banking. This guide provides a comprehensive Germany's open banking overview, its regulatory framework, and adoption trends.
Germany’s Open Banking Regulation
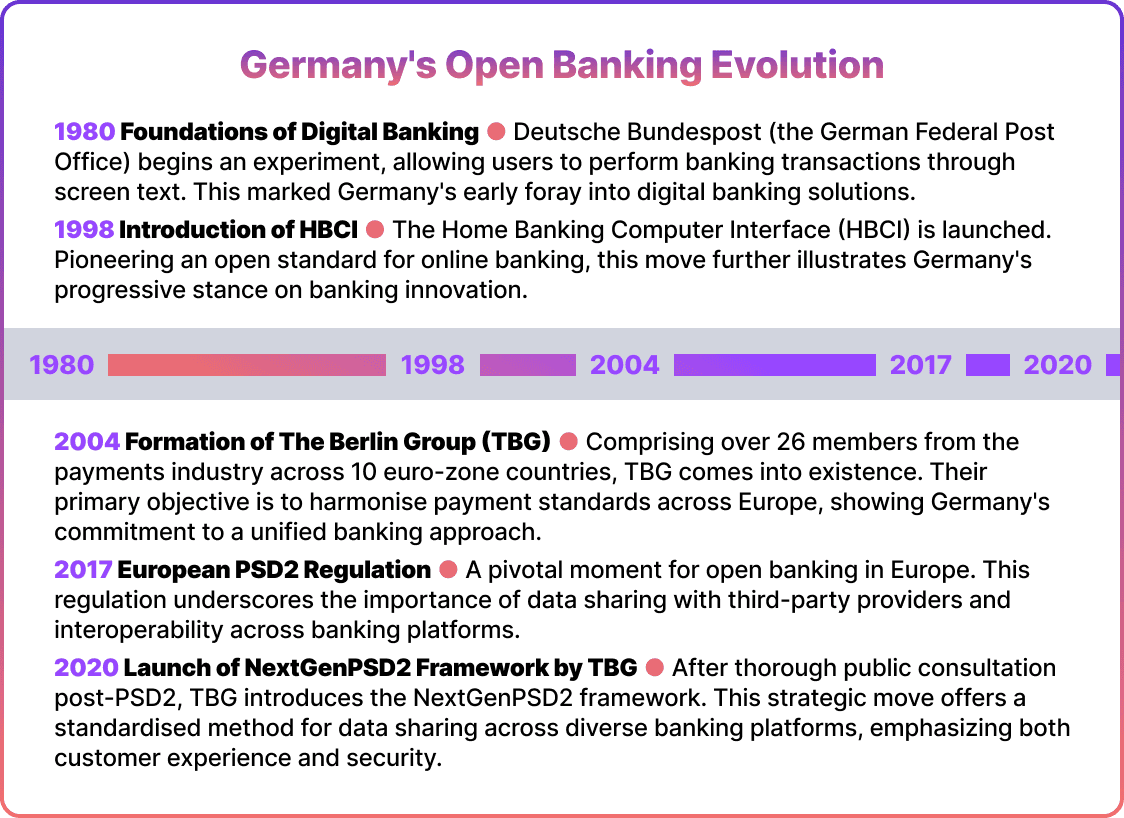
Germany's journey with open banking commenced long before it became a widespread term. Back in the late 20th century, Germany was already exploring digital banking solutions.
In 1980, the Deutsche Bundespost (or the German Federal Post Office) initiated an experiment that allowed users to conduct banking transactions through screen text. This early endeavor served as the foundation for more advanced systems.
Then, in 1998, Germany introduced the Home Banking Computer Interface (HBCI), which pioneered an open standard for online banking. These initial advancements showed the country’s openness to innovation.
The Berlin Group (TBG) played a crucial role in shaping the open banking landscape not only in Germany but throughout Europe. TBG is a collaboration of more than 26 players in the payments industry from 10 different euro-zone countries. They are essentially banks (ASPSPs), banking associations, payment associations, national and international payment schemes, and interbank processors. Founded in 2004, TBG aimed to establish harmonised payment standards that span across Europe. Their efforts complement other European initiatives, fostering a cohesive approach towards open banking.
After the introduction of European PSD2 regulation for the open banking ecosystem in 2017, TBG launched an extensive public market consultation. Based on its feedback, in 2020 the group published the NextGenPSD2 rules offering a standardised approach to seamless data sharing between diverse banking platforms, prioritising customer experience and security. Although it’s optional for banks in Germany, its widespread adoption speaks volumes about its effectiveness and the industry's trust in TBG's visionary goals.
Between 2023 and 2025, Germany’s open banking ecosystem matured even more rapidly, driven by both regulatory momentum and private-sector innovation. In 2023, the European Commission unveiled draft legislation for PSD3, the PSR, and FiDA, aiming to expand the scope of open banking into open finance. Germany responded by improving API infrastructure, such as the Berlin Group's updated frameworks, and saw a surge in fintech growth, with over 950 fintech start-ups operating in the country by year’s end.
By 2024, momentum shifted toward real-time payments and wallet-based innovations. German banks partnered in the launch of Wero, a pan-European instant payment app under the European Payments Initiative (EPI), and retired legacy schemes like giropay/paydirekt. The German Banking Industry Committee (GBIC) supported this shift with the rollout of giroAPI, a unified interface for third-party access to payment initiation and account data, cementing Germany’s position as a leader in open banking infrastructure.
In 2025, regulatory transitions began to materialise. SEPA Instant became free to receive across the Eurozone, opening the door for broader adoption of account-to-account (A2A) payments. Germany also influenced negotiations on the Financial Data Access (FiDA) proposal, advocating longer transition periods and more focused data scopes. Meanwhile, banks and fintechs prepared for the broader open finance ecosystem with upgraded APIs and strong customer authentication, positioning Germany at the forefront of the EU’s digital financial transformation.
Open Banking Market in Germany: Adoption Rates
Germany's position in the open banking landscape is significant. According to Yapily's 2022 European Open Banking League Table, Germany ranks second only to the UK with a score of 8.2. This ranking underscores the country’s proactive approach and commitment to seamlessly integrating open banking into its financial ecosystem.
As of 2025, Germany remains a key player in Europe’s open banking ecosystem. Through ongoing regulatory reforms and infrastructure upgrades such as the rollout of giroAPI and the adoption of SEPA Instant across major banks, it continues to hold a top-tier position. According to Yapily, Germany is now widely recognised for its stable API performance and strong developer support, positioning it among the most open-banking-ready nations in the EU.
Adoption has also accelerated markedly. Following the groundwork laid during the pandemic, digital payment usage has become mainstream. A 2024 Bundesbank report shows that 68% of Germans now regularly use digital payments for day-to-day transactions, up from 65% in 2020. This uptake is reinforced by real-time payment capabilities and the emergence of Wero, a European-wide wallet launched under the European Payments Initiative (EPI).
Germany’s fintech sector has also scaled rapidly – by 2024, the country hosts over 950 active fintech companies. These developments highlight Germany’s transformation into a highly competitive, innovation-driven market for open banking and digital finance.
The adoption of open banking in Germany has seen remarkable growth. The global pandemic played a crucial role by accelerating the shift towards digital banking solutions. A study conducted by Mastercard shed light on this transformative change. In 2020, a significant 65% of Germans increased their use of digital payments, and this trend continues to surge.
Meanwhile, Germany's fintech sector is experiencing a remarkable boom. The country currently boasts more than 700 active fintech startups, evidencing its rapid drive towards digital innovation. With a transaction value of $232.5 billion in 2022, digital payments constitute a significant segment within the fintech market.
Open Banking Benefits for Germany
Open banking represents more than just a technological advancement. It signifies a paradigm shift that brings forth numerous advantages for businesses, consumers, and the entire financial ecosystem. Here are some key benefits currently being experienced in Germany:
- Cost Efficiency: Open banking, particularly with Account-to-Account (A2A) payments, has the potential to greatly reduce transaction costs for merchants by eliminating card schemes. Traditional card payments often involve various fees imposed by card issuers, which can increase the overall cost of transaction processing. Open banking technology provides a more financially advantageous option.
- Competition: Market competition increases due to the implementation of open banking. This framework allows various payment service providers to enter the market and offer competitive prices. As a result, consumers have more choices and can enjoy better rates for services.
- Improved Security: The foundation of open banking lies in ensuring the utmost security. All third-party payment service providers strictly adhere to rigorous security standards in order to operate. This has resulted in a more transparent banking sector, with standardised security procedures and shared data enhancing overall safety.
- Enhanced Authentication: Open banking has strengthened the process of verifying consumer identities. The introduction of Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) provides an additional layer of security for all electronic payments, effectively lowering the risk of payment fraud.
- Personalised Services: Open banking enables the tailoring of services to meet individual client needs, resulting in more efficient daily operations. The availability of various banking APIs automates processes, effectively saving time and resources.
Future of Open Banking in Germany
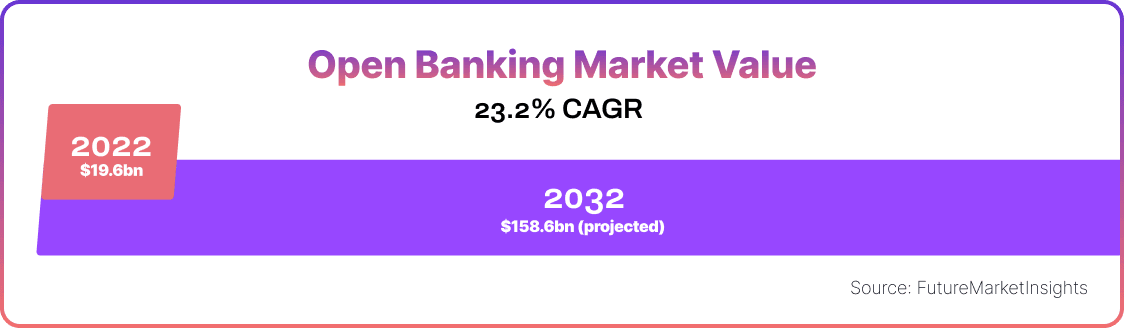
Germany is poised for a transformative era in open banking, which is predicted to grow to $158.6bn market value worldwide by 2032.
With the evolving financial landscape, there are several key trends and predictions that give a promising outlook for the future.
Personalisation and Customisation
Open banking in Germany is showing promising growth. The consolidation of banking services, along with the rising demand in the financial market, is expected to drive market expansion. As more individuals and businesses realise the advantages of open banking, its adoption is projected to increase significantly.
Growth in Value-Added Services
Value-added services are expected to experience a substantial growth rate of 11.3% in the open banking landscape. These services, which leverage artificial intelligence and data science, will provide users with valuable insights that will attract businesses and consumers alike.
Shift to Cloud Deployment
The adoption of cloud deployment is expected to experience substantial growth, with an estimated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.7%, according to FutureMarketInsights. This shift is being driven by the desire for businesses to minimise investments in physical space, hardware, and software technologies. From cost savings to increased scalability, both small and large enterprises are recognizing the advantages that come with embracing cloud deployment.
Dominance of the App Market
Finally, the app market, which had the largest market share of 33.8% in 2021, will maintain its dominance. With more and more fintech companies conducting their operations through smartphones, there will be a significant increase in demand for open banking apps. These apps offer consumers convenient access right at their fingertips.
Conclusion
Germany's embrace of open banking demonstrates its dedication to progress and innovation. As the advantages become increasingly apparent, more people will choose to adopt this approach, transforming the financial industry.
The future of open banking in Germany looks promising, as experts predict substantial market growth and improved services through the implementation of more efficient technologies. It is vital for business leaders and executives to stay informed about these advancements in order to remain competitive. Embracing open banking is not only about staying ahead; it also paves the way for a transparent, efficient, and customer-focused financial future.
Why choose Noda for Germany?
Germany is one of Europe’s largest e-commerce markets, with high digital banking usage and increasing demand for seamless, secure payments.
Why choose us for Germany:
- Broad bank connectivity
Connect to a wide network of German and 2000+ European banks through a single, unified integration. - Low transaction costs
Benefit from highly competitive fees (from 0.1% per transaction) that help you maintain strong margins. - Fast settlement
Receive funds in seconds via instant account-to-account transfers—no intermediaries, no delays. - Quick integration
Launch effortlessly with plugins for the leading e-commerce platforms (WooCommerce, Magento, OpenCart, and PrestaShop), or build a custom solution via our flexible API. - All-in-one payments
Offer open banking, cards, Apple Pay, Google Pay and more—seamlessly in one platform. - No-code solutions
Generate payment links and QR codes instantly — accept bank payments without a website or any integrations required. - Personalised support
An ongoing personal manager support to ensure your success.
Contact Noda for a no-obligation demo. Our open banking experts will be happy to look into your unique business case.
FAQs
Does Germany have open banking?
Yes. Germany has implemented PSD2 since 2018. Banks provide regulated access to AIS and PIS through developer portals in line with EU standards.
Is open banking legal in Germany?
Absolutely – it falls under PSD2 and GDPR, supervised by BaFin, with strict requirements for eIDAS certificates and Strong Customer Authentication (SCA).
Is open banking safe in Germany?
Yes. All access requires user consent and SCA, with security frameworks that meet EU regulatory and technical standards.
Which banks offer PSD2 APIs in Germany?
All major banks in Germany offer PSD2-compliant APIs, ensuring secure, regulated access to account and payment services.
Latest from Noda

Payment Methods in Ireland in 2026: Everything You Need to Know

Top Payment Methods in Austria: How to Accept Payments Efficiently in 2026

GoCardless Review 2026: What Merchants Need to Know


