Open Banking and PSD2 are terms that can be confusing for many. Though they relate to one industry, they aren't the same. But what exactly do they mean, where are the overlaps, and what’s the key difference? In this overview, we take a look at the meanings behind PSD2 and open banking.
What is Open Banking?
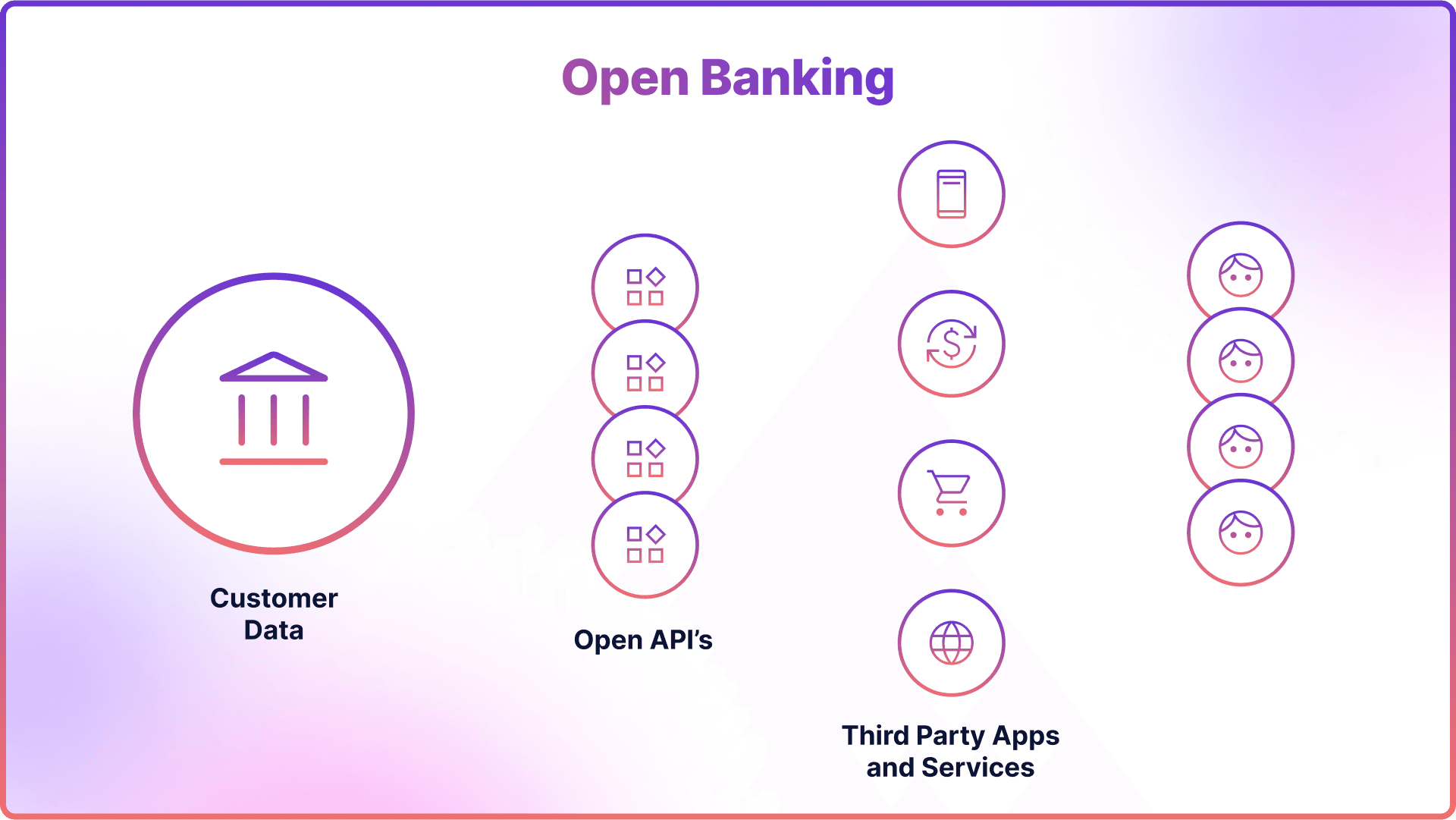
Open banking is an innovative initiative aimed at reshaping the banking industry. Its fundamental principle involves granting regulated third-party providers (TPPs) access to and control over consumers' bank accounts, thereby offering a more transparent and streamlined approach to managing transactions.
The ultimate objective of this system is to promote competition and foster innovation within the banking sector. By integrating with numerous applications such as banking, e-commerce, money management, and payment processing platforms through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), open banking provides consumers with enhanced access to their financial data.
In the realm of open banking, APIs play a crucial role in enabling seamless communication between different software applications. For example, a third-party financial app can use an API to securely request access to customer bank account data, provided their consent.
User consent and data protection are key components of API sharing in open banking. In order for any third-party application to access a user's data, explicit permission must be obtained from the user. This ensures that consumers have complete control over who can access their financial information.
Open Banking Initiative in the UK
Open Banking is also a term that refers to the open banking initiative in the UK. While open banking as a general concept denotes the broader idea of sharing financial data, the UK's Open Banking initiative is a specific regulatory mandate.
The initiative, introduced by the UK's Competition and Markets Authority (CMA), required the nine largest banks in the UK to securely share customer data in a standardised format, with the customer's consent. It led to the establishment of the Open Banking Implementation Entity (OBIE) (currently renamed Open Banking Limited), which sets industry standards and guidelines to drive competition and foster innovation.
What is PSD2?
PSD2, or the Revised Payment Services Directive, is an updated EU legislation that seeks to improve the security standards for online transactions. Building on the initial Payment Service Providers Directive (PSD), PSD2 aims to promote the growth of alternative digital payment methods on different devices like mobile phones, computers, and tablets. It came into force in 2018.
An important component of PSD2 is its focus on allowing third-party financial service providers to access consumer account information without having to go through the bank's online portal. This crucial change enabled the concept of open banking throughout Europe. Under PSD2, banks are required to provide open APIs that allow cross-platform access to customers' accounts and payment data, but always with the explicit consent of the consumer.
PSD3 Explained
Meanwhile, in June 2023, the European Commission introduced its draft legislation for the Third Payment Services Directive (PSD3) to build on the progress made since the introduction of PSD2.
Building on this foundation, PSD3 shifted from a directive to a regulation, aiming for consistent implementation across the EU member states. This change seeks to establish a more unified payments market and minimise discrepancies between countries. The directive focuses on enhancing the open banking ecosystem by improving API quality and performance, as well as simplifying authentication processes. It is expected that the directive will be finalised by 2025 and enforced by 2026.
What is the Difference Between Open Banking and PSD2?
Open banking is a global concept that aims to facilitate secure and agreed-upon electronic sharing of financial data. It represents a movement towards greater interconnectedness in the financial ecosystem.
On the other hand, PSD2 is a specific European legislation that establishes the legal framework for open banking practices across Europe. The UK's Open Banking initiative is a mandate within PSD2 focused on standardising data sharing among major banks in the UK.
Essentially, while open banking provides the overall blueprint, PSD2 offers the necessary legal foundation, and the UK's Open Banking sets a specific standard for its local implementation.
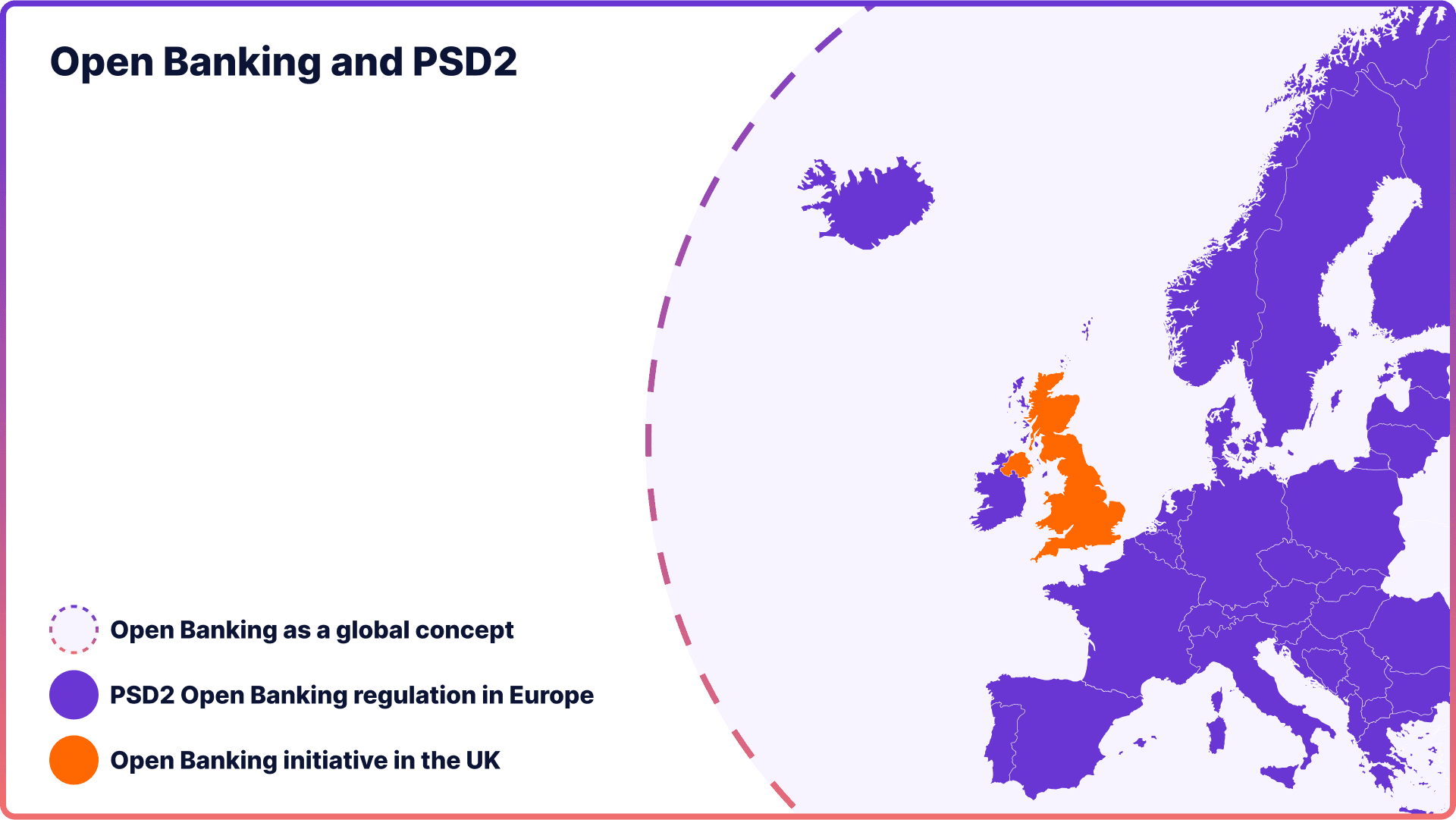
PSD2 vs Open Banking in the UK
- Origin & Scope: PSD2 is an EU-wide regulation applicable to all member states. Meanwhile, Open Banking in the UK is a specific initiative mandated by the UK's Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) to implement PSD2.
- Data Sharing: PSD2 mandates banks to open up their payment systems and customer data to third parties but doesn't dictate a standardised approach. Open Banking in the UK requires the nine largest banks (CMA9) to share data in a standardised format using dedicated APIs.
- Technical Standards: PSD2 provides a broad legal framework without prescriptive technical standards. Open Banking in the UK prescribes specific technical standards for data sharing, ensuring consistency across banks.
- Implementation: PSD2 is a flexible directive, allowing member states to adapt and implement based on their regional needs. Open Banking in the UK is a more prescriptive approach, with clear guidelines and timelines for the participating banks.
Open Banking With Noda
Elevate your business with Noda’s payments and open banking solution. Drive increased sales and save valuable time through streamlined processes. Our all-in-one platform prioritises customer understanding, efficient operations, and growth
Noda is a worldwide payment and open banking provider for seamless business transactions. From payment facilitation and AI-powered financial analytics for businesses to customer clustering and user-friendly verification, Noda has got you covered. Our platform uses cutting-edge AI and machine-learning technologies. Unlock your business potential with Noda - your payments are our priority.
Final Thoughts
To fully grasp the ongoing transformation in the financial sector, it's important to understand the distinctions between open banking as a global concept, the UK's Open Banking initiative, and PSD2.
While open banking signifies a worldwide shift towards transparent and interoperable financial services, the UK's Open Banking initiative takes a structured approach specific to the nation. It emphasises standardised data sharing among major banks within the country.
On the other hand, PSD2 serves as the European regulatory foundation that supports and mandates open banking practices across Europe. By analysing these elements together, we can better appreciate the multifaceted nature of the financial sector's evolution and its role in shaping an interconnected and consumer-centric future.
Latest from Noda
Digital Payment Trends: Navigating the Future

Payment Methods in Ireland in 2026: Everything You Need to Know

Top Payment Methods in Austria: How to Accept Payments Efficiently in 2026


